Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
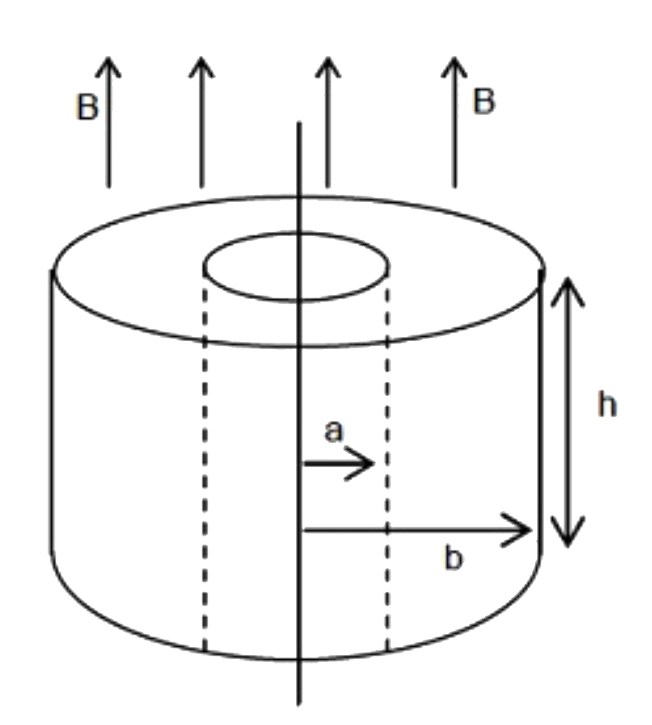
- A conducting ring of circular cross - section with inner and outer rad...
Text Solution
|
- A magnet is taken towards a conducting ring in such a way that a const...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a conducting ring of radius R. A uniform steady magne...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: Two coaxial conducting rings of different radii are place...
Text Solution
|
- A circular ring of radius r is placed in a homogeneous magnetic field ...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical cylindrical region has a horizontal radial magnetic field i...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting ring of radius r and resistance R is placed in region of ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting ring of circular cross - section with inner and outer rad...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular -conducting ring having N turns of radius R is falling...
Text Solution
|