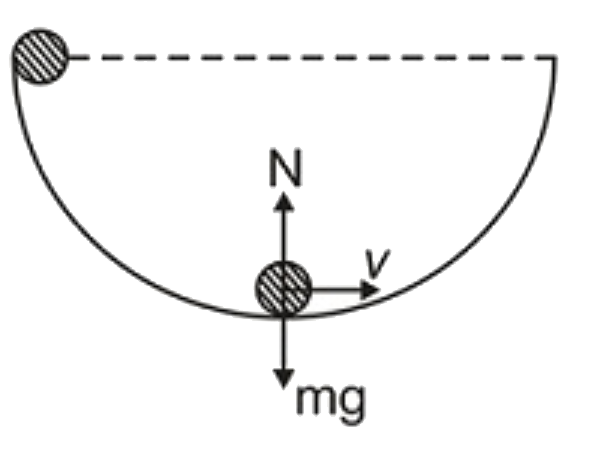
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A solid spherical ball of mass m is released from the topmost point of...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m and radius r rolls inside a fixed hemispherical shell...
Text Solution
|
- A solid ball of mass 'm' is released on a rough fixed inclined plane f...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow cylinder, a spherical shell, a solid cylinder and a solid sph...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m inside a smooth spherical shell of radius R with velo...
Text Solution
|
- Inside a smooth spherical shell of the radius R a ball of the same mas...
Text Solution
|
- In the above probllem, the normal force between the ball and the shell...
Text Solution
|
- A tangential force 'F' is applied at the topmost point of a spherical ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid spherical ball of mass m is released from the topmost point of...
Text Solution
|