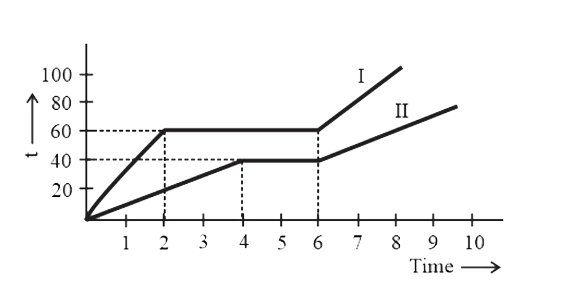
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two bodies of equal masses are heated at a uniform rate under identica...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of equal masses are heated at a uniform rate under identica...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid bodies of equal mass m initially at T = 0^(@)C are heated at...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of equal mass m are heated at a uniform rate under identica...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid spheres are heated to the same temperature allowed to cool u...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid spheres of radii R(1) and R(2) are made of the same material...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of different materials but of equal mass are heated at unif...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies A and B of equal masses are supplied with equal amountt of ...
Text Solution
|
- The thermal capacities of two bodies A and B are in the ratio 1:4. if ...
Text Solution
|