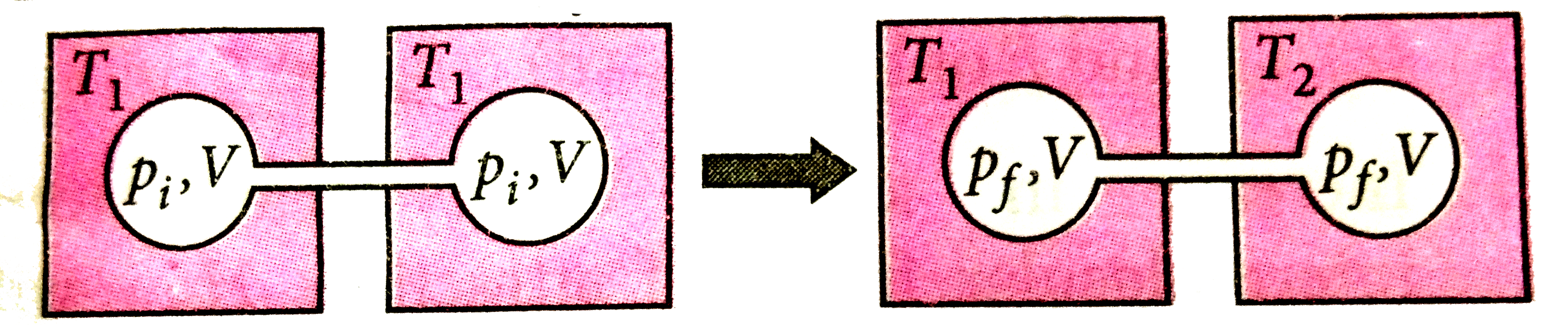
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially...
Text Solution
|
- shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gas. The p...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed vessels of equal volume containing air at pressure P(1) and...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed vessels of equal volume contain air at P(0) pressure, T(0) ...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed bulb of euqal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially ...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed vessels of equal volume containing air at pressure P(1) and...
Text Solution
|
- समान आयतन (V) के दो बंद बल्ब, जिनमें एक आदर्श गैस प्रारंभिक दाब p(i) त...
Text Solution
|