A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The spectral emissive power E(lambda) for a body at temperature T(1) i...
Text Solution
|
- Shown below are the black body radiation curves at temperature T(1) an...
Text Solution
|
- The spectral emissive power E(lambda) for a body at temperature T(1) i...
Text Solution
|
- The adjoining diagram shows the spectral energy density distribution E...
Text Solution
|
- A black body emits maximum radiation of wavelength lambda(1) at a cert...
Text Solution
|
- The stress-strain graph for a metallic wire is shown at two different ...
Text Solution
|
- दो पिण्ड विभिन्न तापों T(1) व T(2) पर हैं । यदि उन्हें उष्मीय संपर्क ...
Text Solution
|
- T(1) is the temperature of oxygen enclosed in a cylinder. The temperat...
Text Solution
|
- Ultraviolet light of wavelength lambda(1) and lambda(2) (with lambda(2...
Text Solution
|
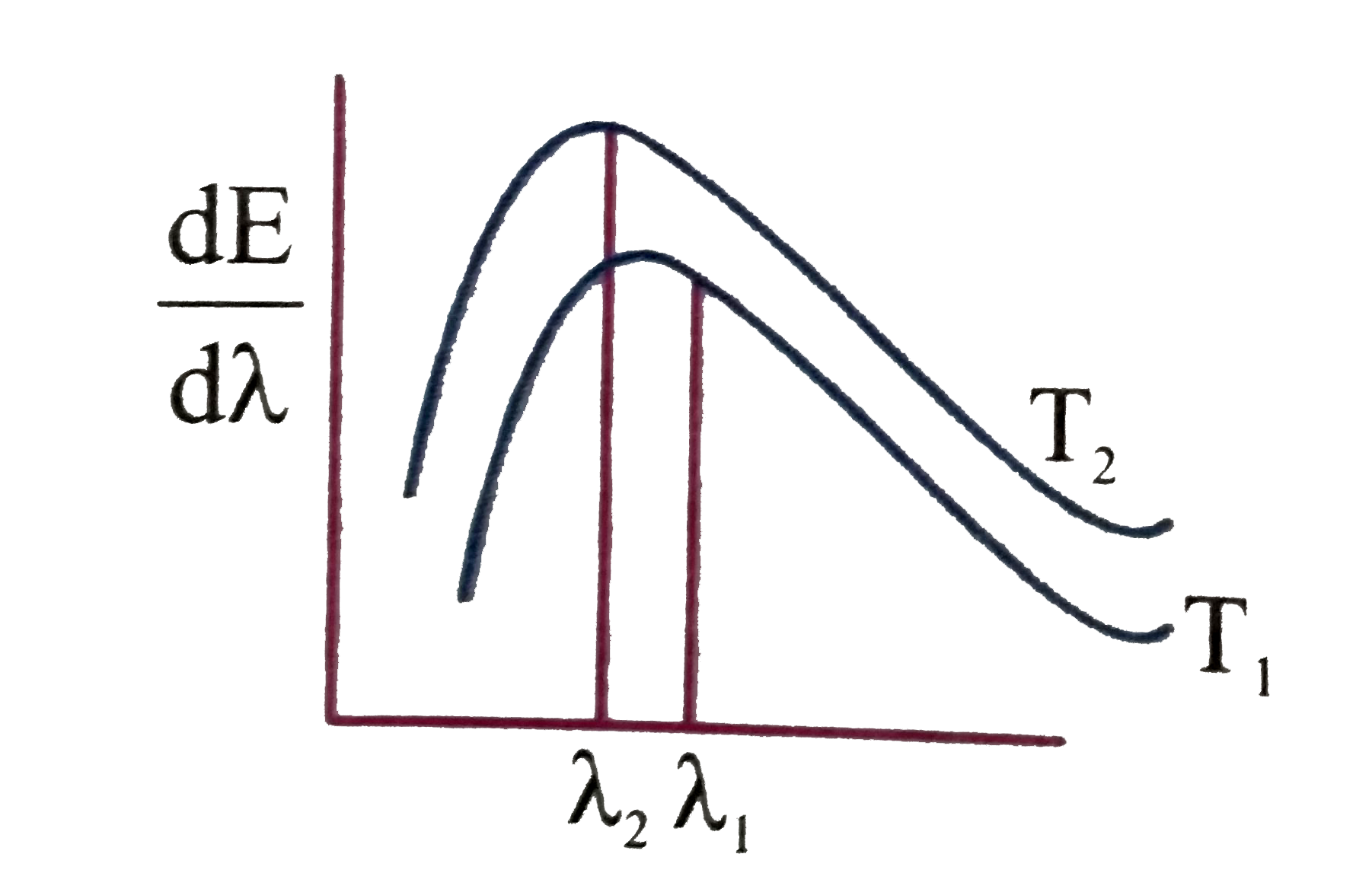 .
.