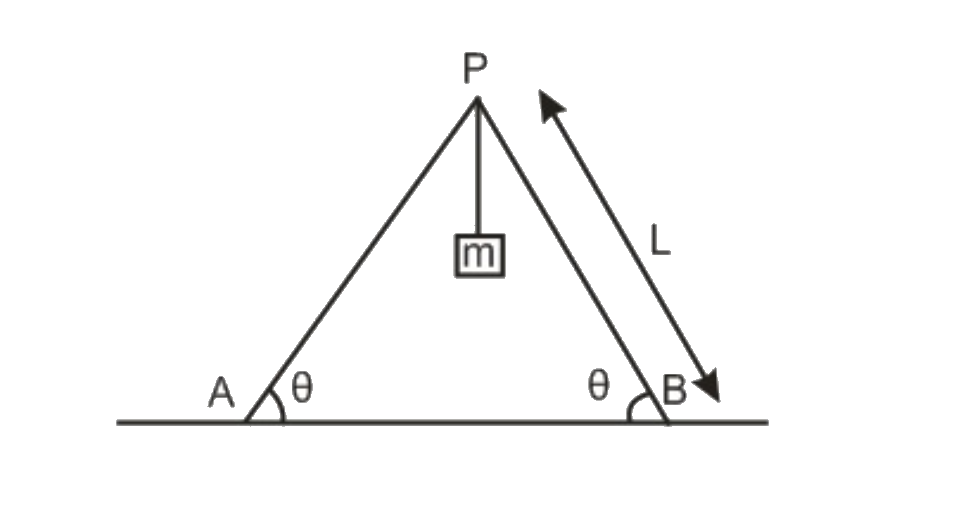
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two identical ladders are arranged as shown in the figure. Mass of the...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, a ladder of mass m is shown leaning against a wall. It ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ladders, each of mass M and length L are resting on the ...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder of length 5 m is placed against a smooth wall as shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder of length l and mass m is placed against a smooth vertical wa...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall (fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ladders are arranged as shown in the figure. Mass of eac...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ladders, each of mass M and length L are resting on the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ladders are arranged as shown in the figure. Mass of the...
Text Solution
|