A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
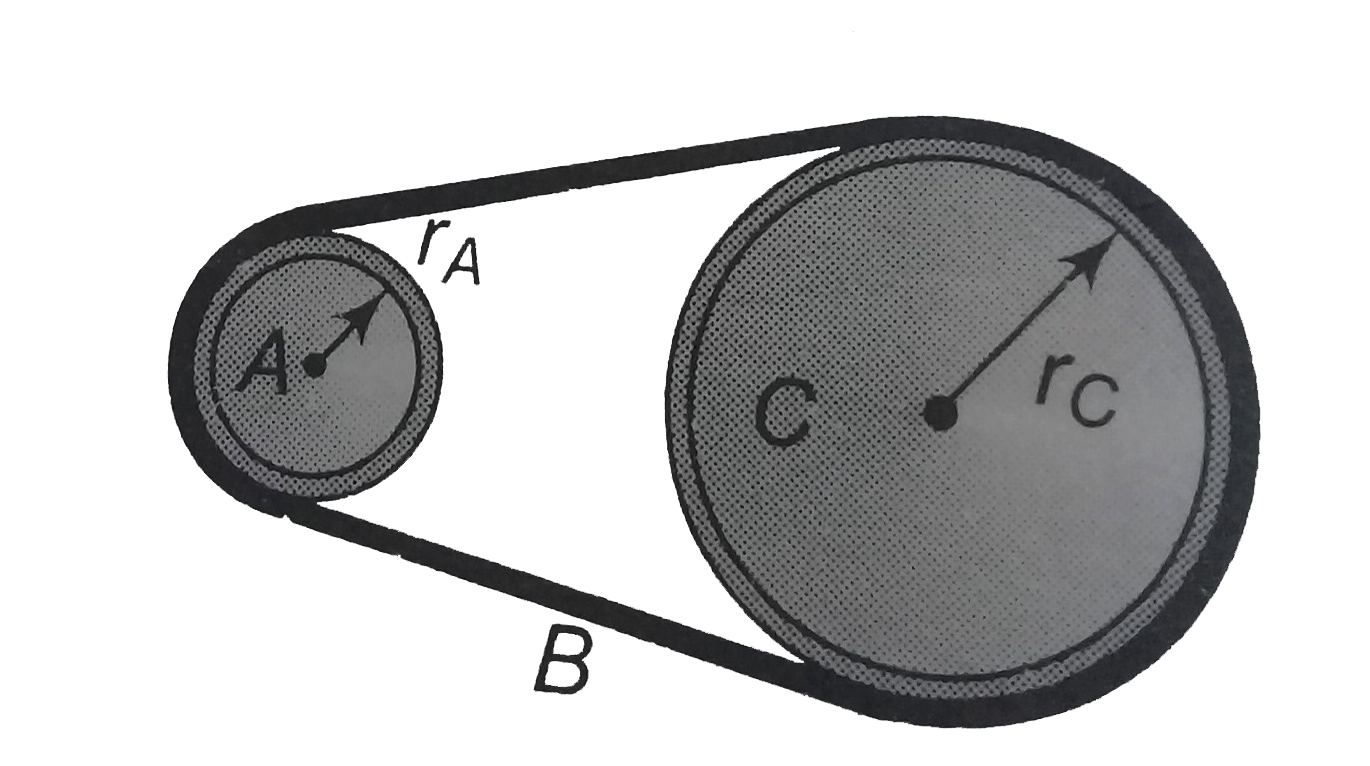
- In figure wheel A of radius rA = 10 cm is coupled by belt B to wheel C...
Text Solution
|
- In figure whell A of radius rA = 10 cm is coupled by belt B to whell C...
Text Solution
|
- Wheel A of radius r(A)=10cm is coupled by a belt C to another wheel of...
Text Solution
|
- A belt passes over a wheel of radius 25 cm. If a point on the belt has...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius 0.1 m (wheel A) is attached by a non-stretching belt...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel having radius 10 cm is coupled by a belt to another wheel of r...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 10-54, wheel A of radius r(A)=10cm is coupled by belt B to whe...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel turns through an angle of 188 rad in 8.0 s, and its angular sp...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel having radius 10cm is coupled by a belt to another wheel of ra...
Text Solution
|
 .
.