A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
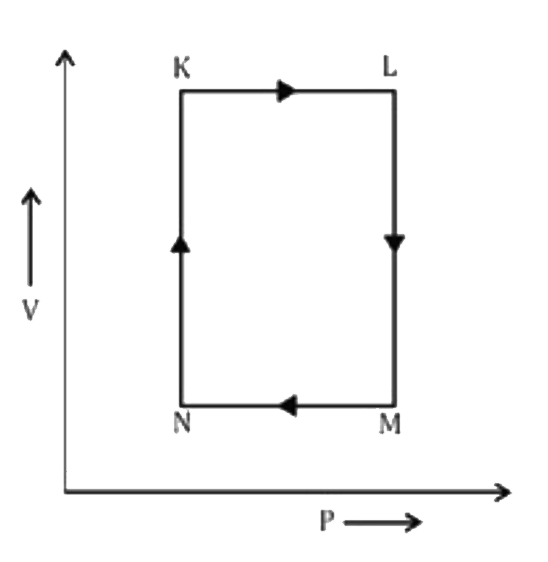
- A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transformation of states from ...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transformation of state: K to ...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transfromation of states from ...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed mass 'm' of a gas is subjected to transformation of states fro...
Text Solution
|
- 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state (1) to state ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m compresses a spring iof stifffness k through a dista...
Text Solution
|
- 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state (1) to state ...
Text Solution
|
- The succeeding operations that enable this transformation of states ar...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transformation of states from ...
Text Solution
|