A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
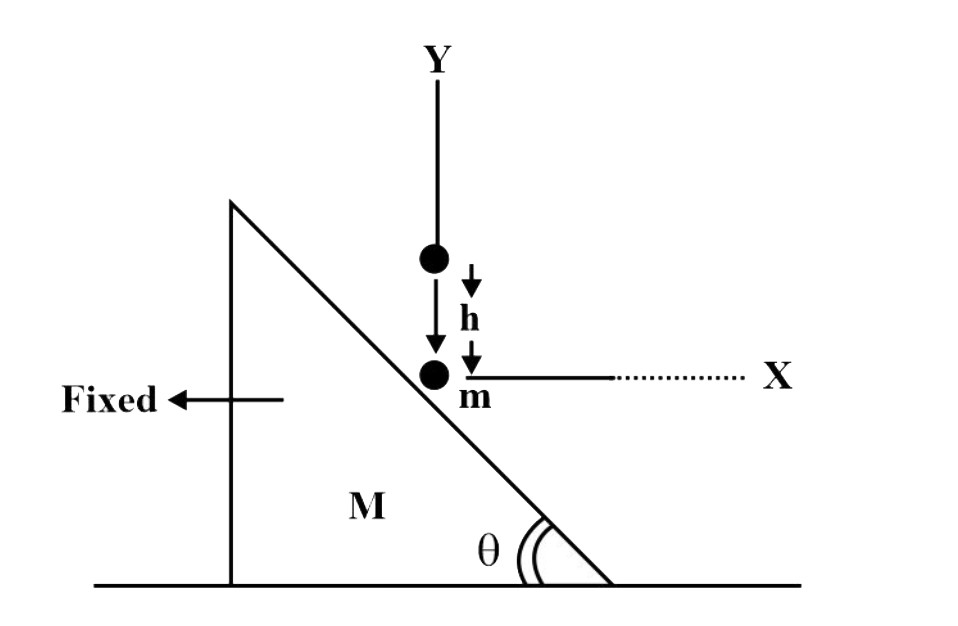
- A ball of mass m is dropped onto a smooth fixed wedge of inclination t...
Text Solution
|
- A ball falls vertically on an inclined plane of inclination alpha with...
Text Solution
|
- A particle (a mud pallet, say) of mass m strikes a smooth stationary w...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m collides with a stationary wedge of mass M, perpendic...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls each of mass 'm' are moving with same velocity v on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- A wedge mass m rest on horizontal surface. The inclination of the wedg...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere P of mass m and velocity vi undergoes an oblique and perfectl...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is dropped onto a smooth fixed wedge of inclination t...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls each of mass 'm' are moving with same velocity v on a smooth...
Text Solution
|