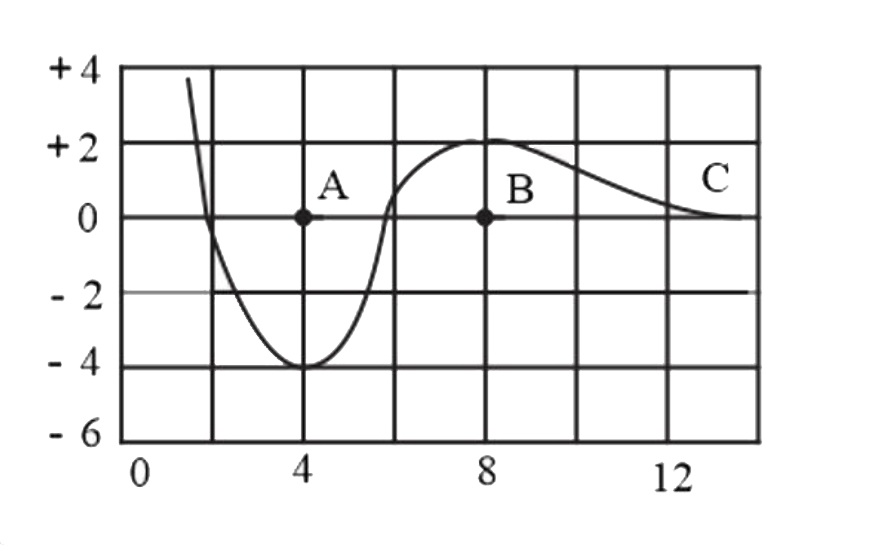
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For the potential energy function shown in fig. there will be an unsta...
Text Solution
|
- For the potential energy curve shown shown in figure. (a) Find directi...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a conservative force field is given by U=ax^...
Text Solution
|
- What is the potential energy of dipole with charge particles system as...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT-1 : If potential energy of a dipole in stable equilibrium po...
Text Solution
|
- For the potential energy function shown in fig. there will be an unsta...
Text Solution
|
- Finding Potential Energy from Force | Finding Force from Potential Ene...
Text Solution
|
- Potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the position (orientations) of a dipole in stable equilibrium,...
Text Solution
|