A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
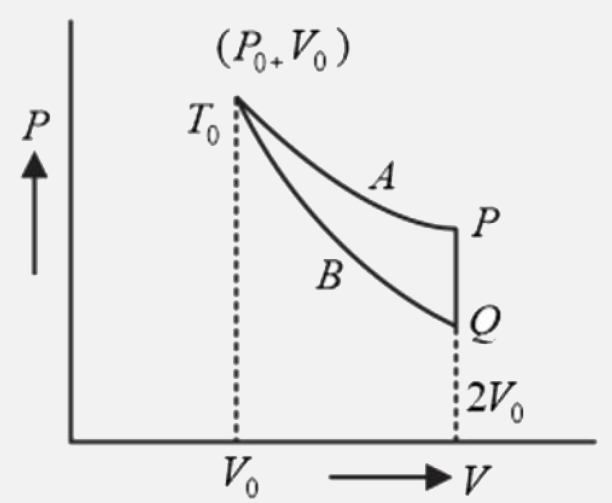
- An ideal gas (1 mol ,monatomic) is in the initial state P (see diagram...
Text Solution
|
- The curves A and B in the figure shown P-V graphs for an isothermal an...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is found to be obeyed the law p^2V = constant . The initial temp...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas (1 mol, monatomic) is in the intial state P (see Fig.) on...
Text Solution
|
- Does the internal energy of an ideal gas change in an isothermal proce...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the work done in the following processes, when gas expands f...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: Temperature of a system can be increased without supplyin...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas at initial temperature T0 and initial volume V0 is expa...
Text Solution
|
- The initial state of 1 mol of an ideal gas is (P(1),V(1),T(1)) . The g...
Text Solution
|