A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
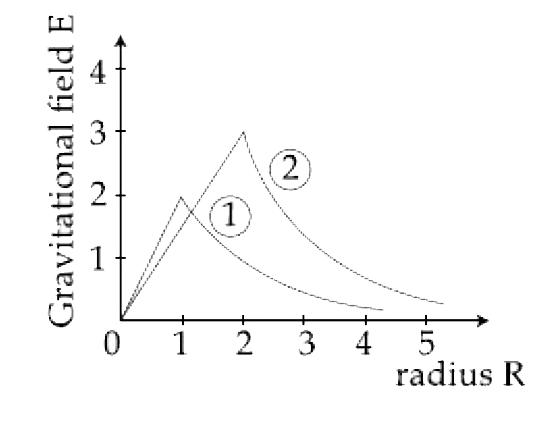
- Consider two solid sphere of radii R(1)=1m, R(2)=2m and masses M(1) an...
Text Solution
|
- Two planets of radii R(1) and R(2 have masses m(1) and M(2) such that ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure represents two concentric shells of radii R(1) and R(2) and...
Text Solution
|
- Supposing Newton's law of gravitation for gravitation force F(1) and F...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two spherical shells have masses m(1) and m(2). Their radi...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two solid sphere oFIGURE radii R(1)=1m, R(2)=2m and masses M(...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric spherical shells of masses and radii m(1), r(1) and m(2...
Text Solution
|
- m(1) तथा m(2) द्रव्यमान (m(1)gt m(2)) के दो उपग्रह पृथ्वी के चारों ओ...
Text Solution
|
- दो साबुन के बुलबुलो की त्रिज्याएँ क्रमशः R(1) व R(2) है , इनके अंदर व...
Text Solution
|