Two smooth blocks are placed at a smooth corner as shown in figure. Both the blocks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block A. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increase `F (theta = 37^(@)` with horizontal).
A soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B becomes zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simultaneously block A will move towards right
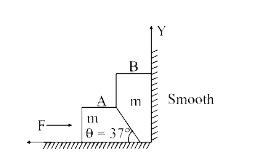
If the acceleration of block A is a rightwards, then the acceleration of block B will
Two smooth blocks are placed at a smooth corner as shown in figure. Both the blocks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block A. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increase `F (theta = 37^(@)` with horizontal).
A soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B becomes zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simultaneously block A will move towards right

If the acceleration of block A is a rightwards, then the acceleration of block B will
A soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B becomes zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simultaneously block A will move towards right

If the acceleration of block A is a rightwards, then the acceleration of block B will
A
Heterocysts
B
Akinetes
C
Gemmule
D
Endospores
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
B
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. If the acceleration of block A is a rightwards, then the acceleration of block B will be
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. If the acceleration of block A is a rightwards, then the acceleration of block B will be
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. If the acceleration of block A is a rightwards, then the acceleration of block B will be
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. What is the minimum value of F to lift block B from ground?
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. What is the minimum value of F to lift block B from ground?
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. If both the blocks are stationary, the force exerted by ground of block A is
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. If both the blocks are stationary, the force exerted by ground of block A is
Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both the bloks are having mass m. We apply a force F on the block m. Block A presses block B in the normal direction, due to which pressing force on vertical wall will increase, and pressing force on the horizontal wall decreases, as we increases F(theta = 37^(@) with horizontal). As soon as the pressing force on the horizontal wall by block B become zero, it will lose contact with ground. If the value of F further increases, block B will accelerate in the upward direction and simulaneously block A will towards right. If both the blocks are stationary, the force exerted by ground of block A is
A block is placed on a smooth inclined plane as shown . For what value of horizontal force F, the block will remain at rest ?
Two block of masses m_(1) and m_(2) are placed side by side on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in fig. A horizontal force F is applied on the block . (a) Find the acceleration of each block. (b) Find the normal reaction between the two blocks.
Recommended Questions
- Two smooth blocks are placed at a smooth corner as shown in figure. Bo...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pressed against a wall which is moving with an ac...
Text Solution
|
- A block weighing w is held against a vertical wall be pressing horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 'M' is pressed against a wall with a horizontal force ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 1 kg is pressed against a wall by applying a horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- संलग्न चित्र में दर्शाये गये दो ब्लॉक A व B, बल F द्वारा दीवार पर दबाय...
Text Solution
|