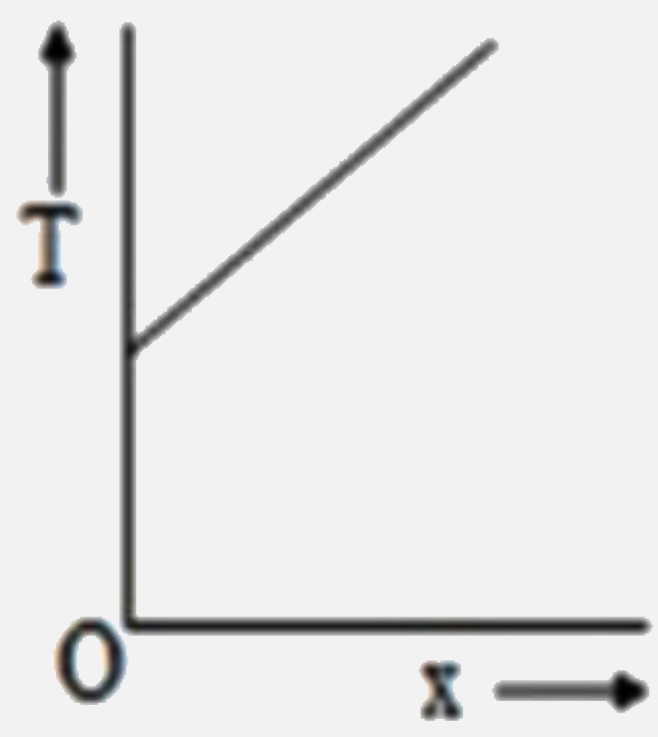
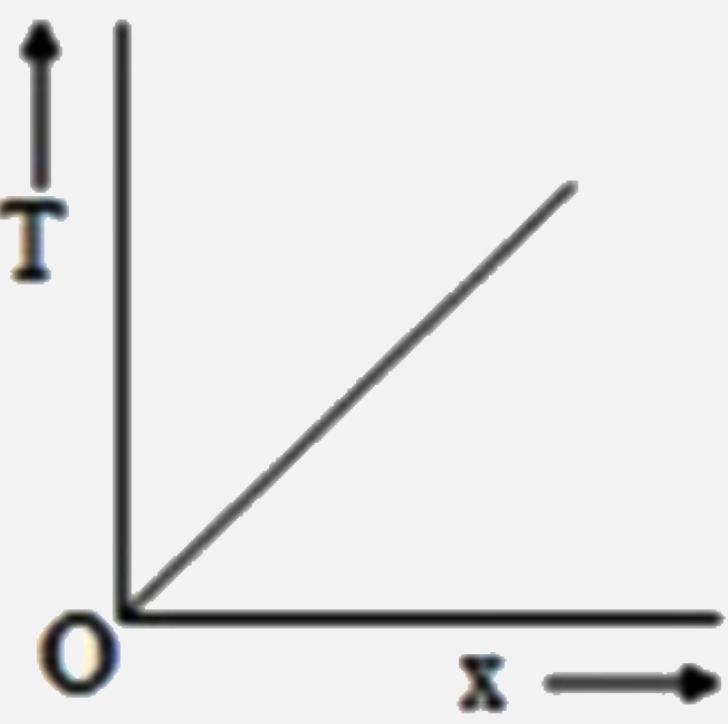
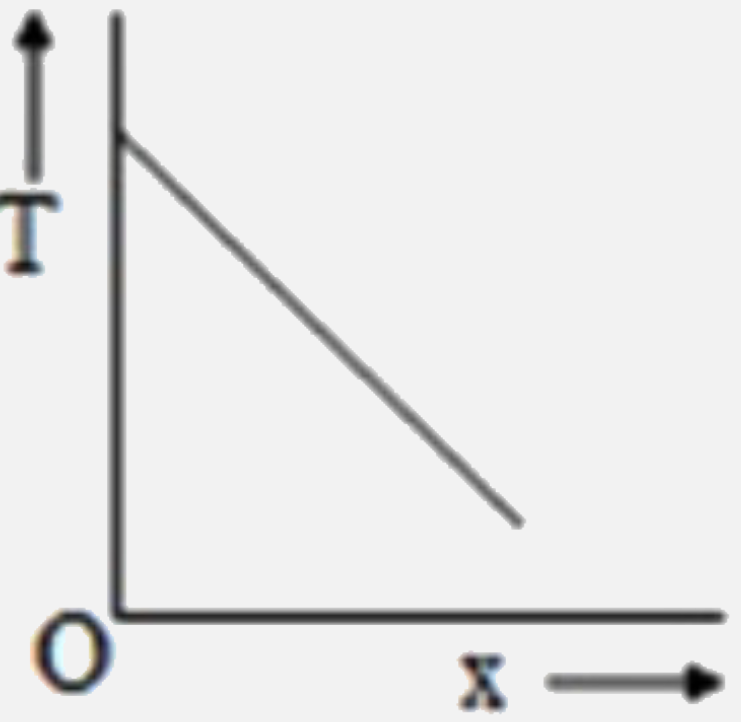
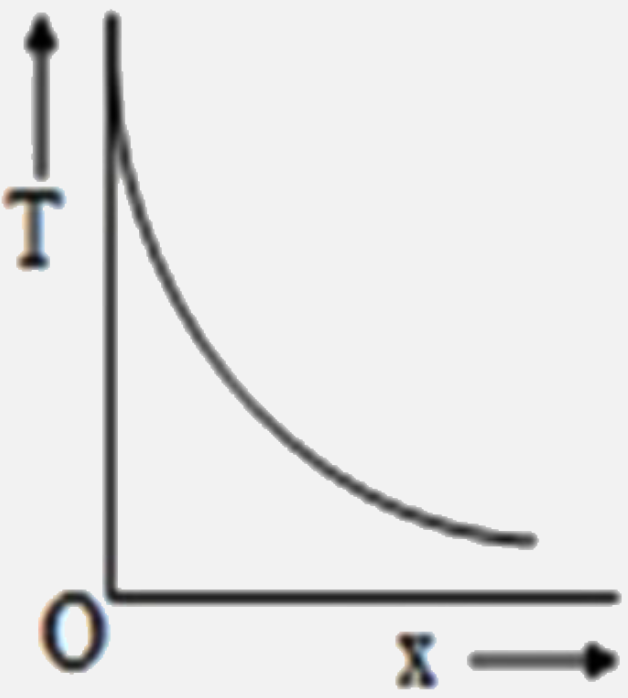
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A conductor of length L is placed along the x - axis , with one of its...
Text Solution
|
- A straight rod of length L has one of its end at the origin and the ot...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical conductor has length l and area of cross section A. Its ...
Text Solution
|
- A conductor of length L is placed along the x - axis , with one of its...
Text Solution
|
- The specific resistance of a material of wire changes as rho = rho(0)x...
Text Solution
|
- Lलम्बाई की छड़ का एक सिरा (x=0) मूल बिन्दु पर तथा दूसरा सिरा (x=L) पर ...
Text Solution
|
- लम्बाई के एक चालक में x=0 से x= 1 दिशा में ऊष्मा प्रवाहित हो रही है। य...
Text Solution
|
- The cross-section area and length of cylindrical conductor are A and l...
Text Solution
|
- The resistivity of cylindrical conductor carrying steady current along...
Text Solution
|