A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
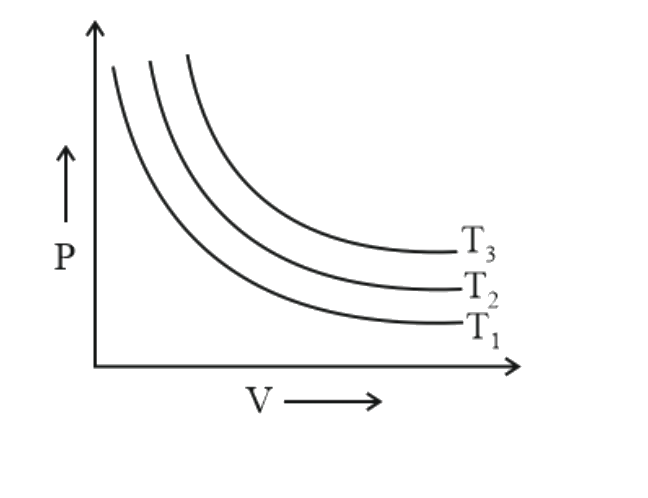
- for the given PV isotherms , which of the following is correct for T1 ...
Text Solution
|
- t1 = (sintheta)^costheta ,t2 = (sintheta)^sintheta , t3 = (costheta)^c...
Text Solution
|
- The vertices of a triangle are [a t1t2,a(t1 +t2)], [a t2t3,a(t2 +t3)],...
Text Solution
|
- for the given PV isotherms , which of the following is correct for T1 ...
Text Solution
|
- The product (PV) is plotted against P at two temperature T1 and T2 and...
Text Solution
|
- The vertices of a triangle are [a t1t2,a(t1 +t2)], [a t2t3,a(t2 +t3)],...
Text Solution
|
- The vertices of a triangle are [a t1t2,a(t1 +t2)], [a t2t3,a(t2 +t3)],...
Text Solution
|
- Write the correct number in the given blanks from the following A.P.1,...
Text Solution
|
- Write the correct number in the given blanks from the following A.P.3,...
Text Solution
|