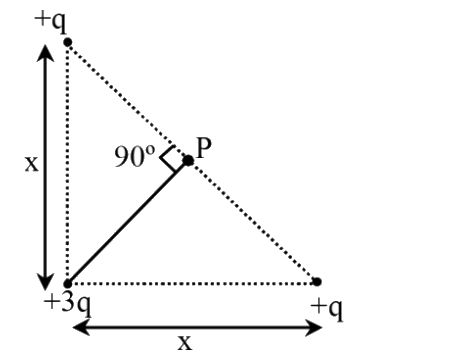
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The magnitude and direction of the electric field at point P can be be...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the electric field lines around an electric dipole. Which...
Text Solution
|
- Evaluate magnitude and direction of magnetic field at a point P in the...
Text Solution
|
- A non-uniform electric field is represented by the diagram. At which o...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a point...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field at a point in space in equal in magnitude to the
Text Solution
|
- The direction of the intensity of the electric field at a point on the...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude and direction of the electric field at point P can be be...
Text Solution
|
- Establish the relation between electric field and electric potential a...
Text Solution
|