A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
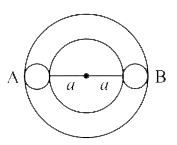
- Two identical spheres A, B are in a smooth horizontal circular smooth ...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal spheres A and B lie on a smooth horizontal circular groove a...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal sphere A and b lie on a smooth horizontal circle groove at o...
Text Solution
|
- Two sphere A and B of equal masses lie on the smooth horizontal circul...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere A impinges directly on an identical sphere B at rest. If coef...
Text Solution
|
- A ball with a velocity of 5 ms^(-1) impinges at angle of 60^(@) with t...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical spheres A, B are in a smooth horizontal circular smooth ...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical spheres lie at rest along a line on a smooth horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- Two sphere A and B of equal masses lie on the smooth horizontal circul...
Text Solution
|