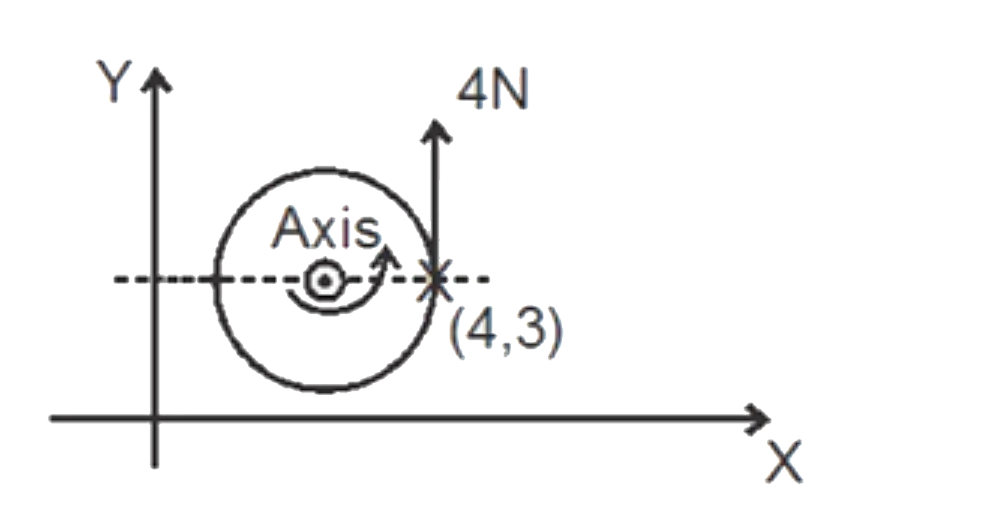
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Consider a uniform disc in the x - y plane free to rotate about an axi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc is rotating at a constant speed in a vertical plane abo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform semicircular disc of mass 'm' and radius 'R' is shown in the...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc is rotating at a constantt speed in a vertical plane ab...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass 4 kg and radius 6 metre is free to rotate in horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius 10 cm can rotate about an axis passing through its ce...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass 2 kg and diameter 40 cm is free to rotate about an axis...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass 4 kg and radius 0.2 m, makes 20 rev/s, about an axis pa...
Text Solution
|
- Find the moment of inertia of a uniform half-disc about an axis perpen...
Text Solution
|