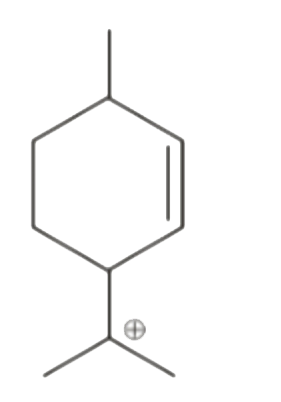
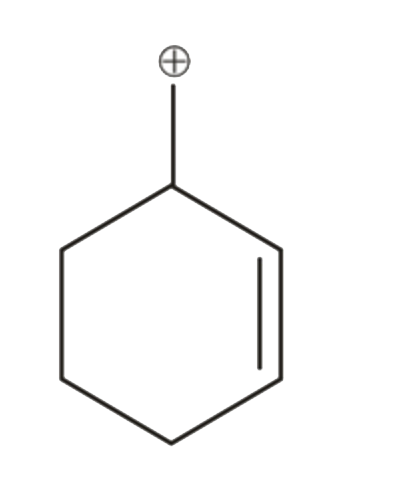
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Which of the following carbocation can not undergo rearrangement ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocation will undergo rarrangement ?
Text Solution
|
- How many carbocation undergoes rearranged
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following in the rearranged in the rearranged more stable...
Text Solution
|
- How many of the following carbocation can undergo rearrangement:
Text Solution
|
- Whenever an intermediate carbocation is formed in reaction it may rear...
Text Solution
|
- Carbocation which does not undergo rearrangement is-
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocations would not likely rearrange to more...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocation can not undergo rearrangement ?
Text Solution
|