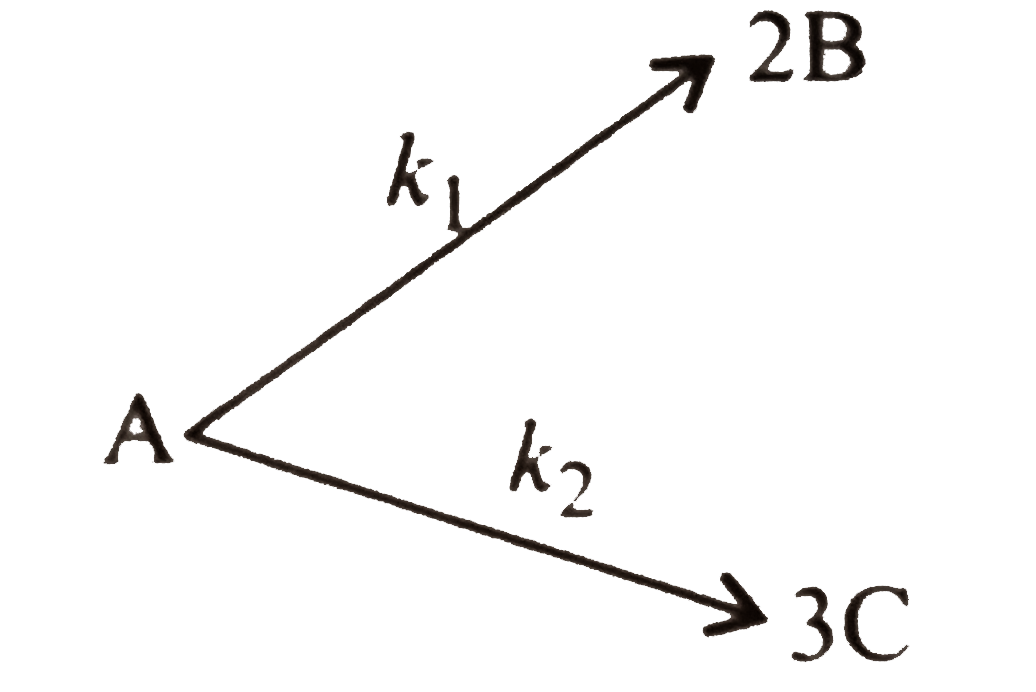
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Consider the following parallel reactions being given by A(t(1//2) = 1...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following parallel reactions being given by A(t(1//2) = 1...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following parallel first order reactions: Half-life of th...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following parallel first order reactions The half-life fo...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A to product the rate of reaction at [A] = ...
Text Solution
|
- दर्शाइए कि प्रथम कोटि की अभिक्रिया में 99.9% अभिक्रिया पूर्ण होने ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that in a first order reaction, time pequired for fompletion of 9...
Text Solution
|
- What is half-life (t(1//2)) of a reaction ? Derive the equations for t...
Text Solution
|
- Half life (t(1/2)) of first order reaction is
Text Solution
|