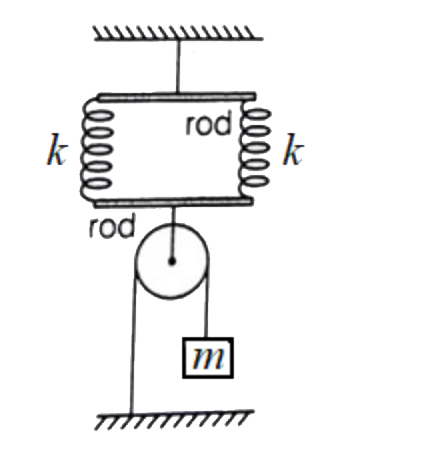
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- There are two identical spring each of spring constant k. here springs...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is suspended as shown in fig. The system is in equilibrium. A...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is connected to another block of mass M by a massles...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs are in a series combination and are attached to a block of...
Text Solution
|
- On a smooth inclined plane a body of mass M is attached between two sp...
Text Solution
|
- On a smooth inclined plane, a body of mass M is attached between two s...
Text Solution
|
- On a smooth inclined plane a body of mass M is attached between two sp...
Text Solution
|
- There are tow identical spring each of spring constant k. here springs...
Text Solution
|
- A spring of spring constant K is cut into two identical pieces...
Text Solution
|