A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
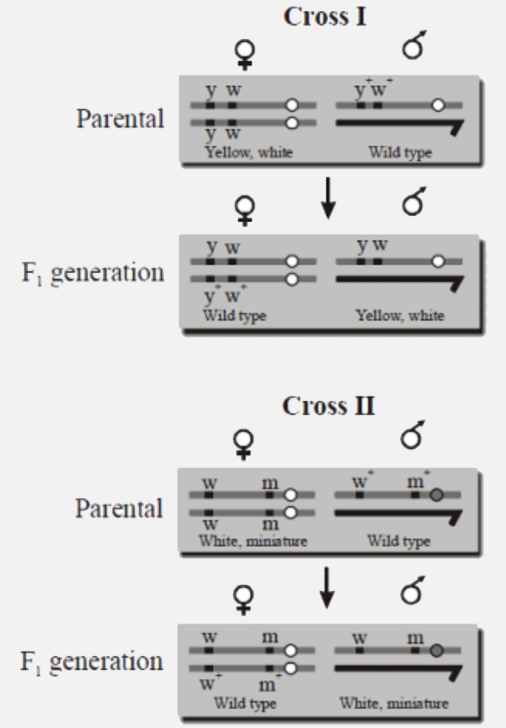
- The figure shows the experiment of T.H Morgan on the linkage. If in cr...
Text Solution
|
- Determination of percentage of crossing over between two linked genes ...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of genes is said to be linked if their recombination frequency ...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of genes are linked if their recombination frequency in test cr...
Text Solution
|
- Morgan caried out several crosses in Drosophila to study genes that we...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements regarding linkage. I. The linked ge...
Text Solution
|
- The coupling and repulsion theory of Bateson and Punnett later on modi...
Text Solution
|
- What are the conclusions drawn by T.H. Morgan from the crossing experi...
Text Solution
|
- Two linked genes and b show 20% recombination the individuals of a hyb...
Text Solution
|