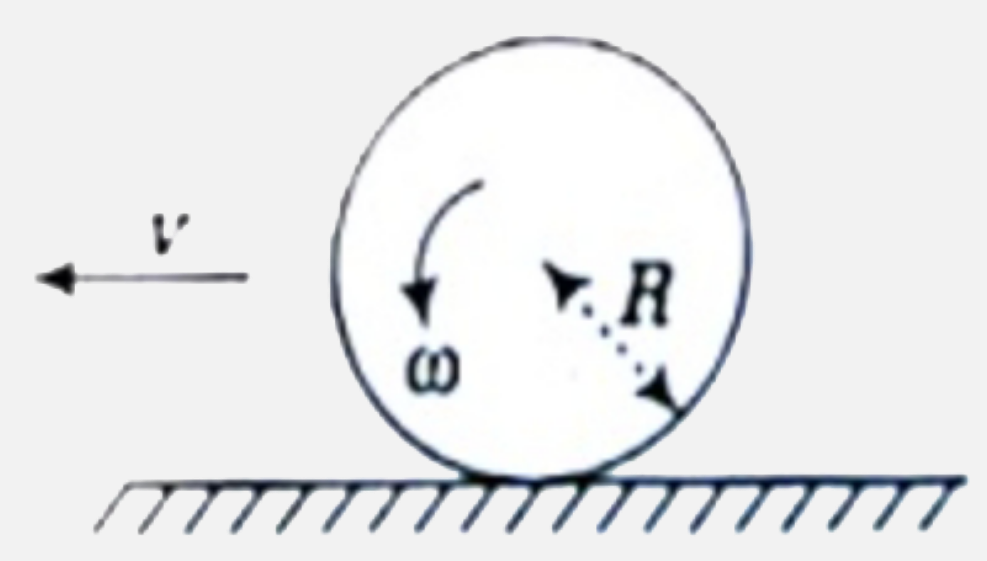
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A tire of radius R rolls on a flat surface with angular velocity omega...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R has linear velocity v and angular velocity omega as...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is taken to a height R from the surface of the earth and then...
Text Solution
|
- A train of mass m moves with a velocity upsilon on the equator from ea...
Text Solution
|
- A body is weighed with a spring balance in a train at rest, shown a we...
Text Solution
|
- Find the relation between the group velocity u and phase velocity upsi...
Text Solution
|
- एक कार R त्रिज्या की वकृत ( curved ) सड़क पर गतिमान है। वह सड़क theta क...
Text Solution
|
- घूर्णन कर रही एक वस्तु में, a=alpha r," और "upsilon=omega r होता है | ...
Text Solution
|
- एक वस्तु शुद्ध घूर्णन गति कर रही है | वस्तु के किसी कण की चाल upsilon ...
Text Solution
|