A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AGRAWAL PUBLICATION-(2019) QUESTION PAPER-EXAMPLE
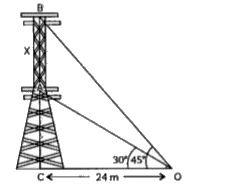
- Radio towers are typically tall structures designed to support antenna...
Text Solution
|
- Check whether g(x) is a factor of P(x) by dividing polynomial p(x) by ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of the equations x-y+ 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y - 12 = 0. Using...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that sqrt 3 is an irrational number.
Text Solution
|
- Find the greatest number which on dividing 1251, 9377 and 15628 leaves...
Text Solution
|
- A,B and C are interior angles of a triangle ABC. Show that sin[(B+C)/2...
Text Solution
|
- If angle A = 90^@, then find the value of tan [(B + C)/2]
Text Solution
|
- If tan(A +B) = 1 and tan(A - B) = 1/ sqrt 3, 0^@ < A + B < 90^@, A>B, ...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, PQ is a chord of length 8 cm of a circle of radius 5 cm. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circel s...
Text Solution
|
- Water in a canal, 6 m wide an 1.5 m deep, is flowing with a speed of 1...
Text Solution
|
- A class teacher has the following absentee record of 40 students of a ...
Text Solution
|
- A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of l...
Text Solution
|
- A pole has to be erected at a point on the boundary of a circular park...
Text Solution
|
- If m times the m^(th) term of an Arithmetic Progession is equal to n t...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of the first three numbers is an Arithmetic Progression is 18....
Text Solution
|
- Construct a triangle ABC with side BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and angle ABC ...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, a decorative block is shown which is made of two solids, a ...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, a decorative block is shown which is made of two solids, a ...
Text Solution
|
- A bucket open at the top is in the form of a frustum of a cone with a ...
Text Solution
|