Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-GRAPHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS-Exercise
- Find the value of k for which the equation x^2 −6x+k=0 has distinct ro...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=tan^(-1)x-cot^(-1)x.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=|x|.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=tan^(-1)x+cos^(-1)x+sin^(-1)x.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of |y|=(x-1)(x-2)(x-3).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=sin^(-1)(x-3).
Text Solution
|
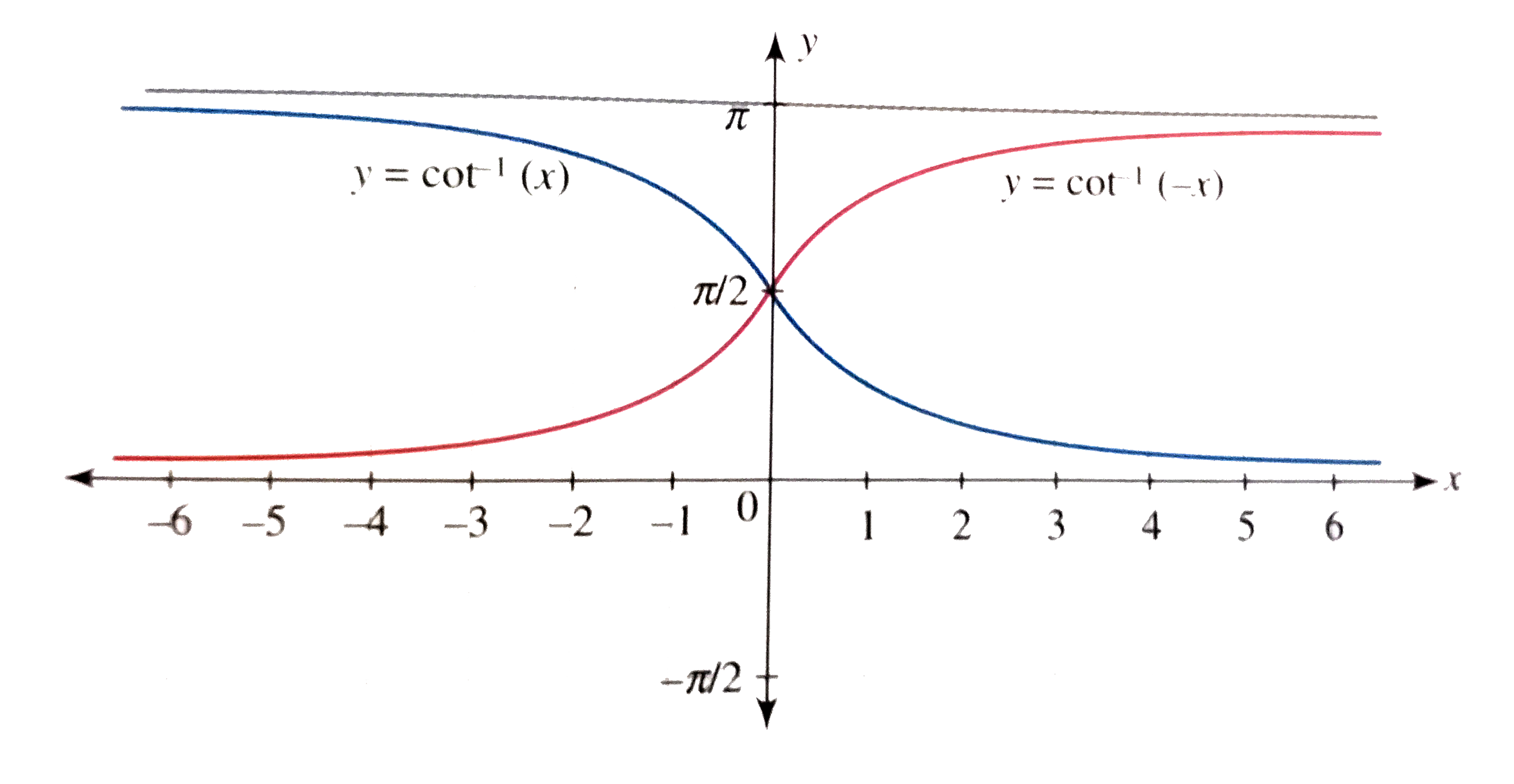
- Draw the graph of y=cot^(-1)x.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=|log(e)(x+3)|.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=|{x}-0.5|, where {.} represents the fractional par...
Text Solution
|
- The number of real solution of the equation sqrt(1+cos2x)=sqrt2 sin^(-...
Text Solution
|
- Find the number of real solutions to the equation log(0.5)x=|x|.
Text Solution
|
- Find the number of points where the function f(x)=max|tanx|,cos|x|) is...
Text Solution
|
- Find the number of points of non-diferentiability for f(x)=max{||x|-1|...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) = max. {|x^2 - 2| x ||,| x |} then number of points where f(x...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of |y|=[x], where [.] represents the greatest integer f...
Text Solution
|