Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY -JEE Previous Year
- If the two lines (x-1)/(2)=(y+1)/(3)=(z-1)/(4)and(x-3)/(1)=(y-m)/(2)=z...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- A plane passes through (1,-2,1) and is perpendicualr to two planes 2x...
Text Solution
|
- Let P(3,2,6) be a point in space and Q be a point on line vec r=( hat...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- If the distance of the point P(1,-2,1) from the plane x+2y-2z=alpha...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- Two lines L1x=5, y/(3-alpha)=z/(-2)a n dL2: x=alphay/(-1)=z/(2-alpha) ...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- In R^(3) let L be straight line passing through the origin. Suppose t...
Text Solution
|
- In R(3) , consider the planes P(1):y=0and P(2) : x+z=1. Let P(3) ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the planes 3x-6y-2z=15a n d2x+y-2z=5. Statement 1:The parame...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- Consider the line L 1 : (x +1)/3 = (y +2)/1 = (z+ 1)/2, L2 : (x-2)/1...
Text Solution
|
- Find the direction cosines of the vector 3hati+2hat j+hat k
Text Solution
|
- If f(x)=3x-2 and g(x)=2x+a and if fog=gof, then find the value of a
Text Solution
|
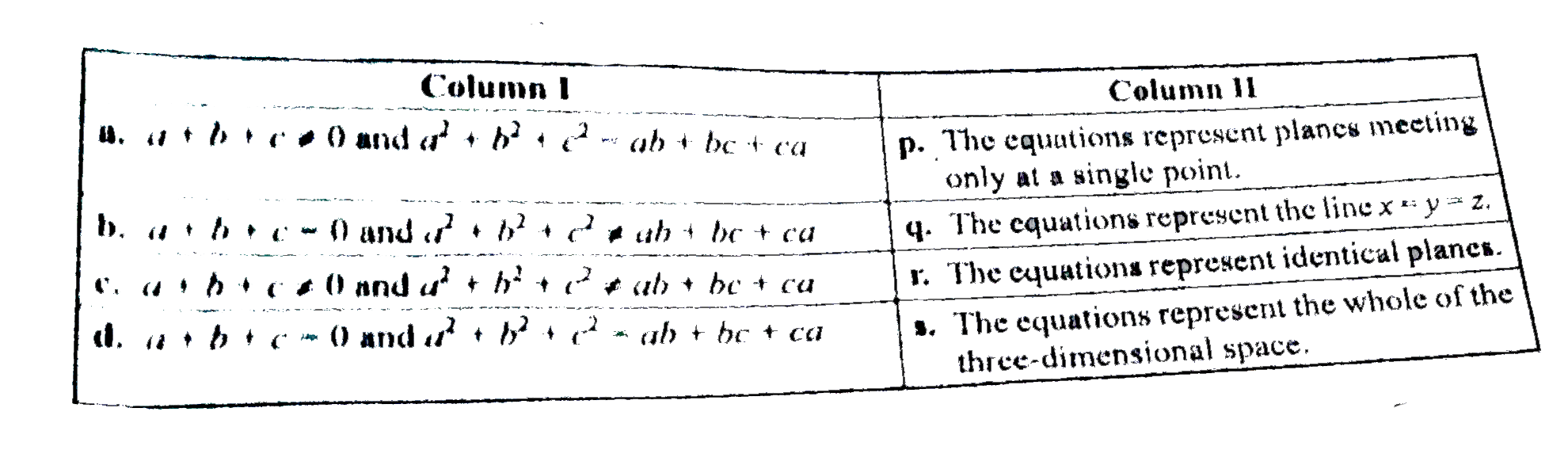
- Consider the linear equations ax+by+cz=0, bx+cy+az=0 and cx+ay+bz=0. ...
Text Solution
|
- Let f:R→R:f(x)=x^2 and g: R→R: g(x)=(x+1). Show that (gof)≠(fog).
Text Solution
|
- If the distance between the plane Ax 2y + z = d and the plane contain...
Text Solution
|