`d(P,L_(1)) = (|x-y|)/(sqrt(2))`
`" and " d(P,L_(2)) = (|x+y|)/(sqrt(2))`
Now, we have
`2 le d(P,L_(1))+d(P,L_(2))le 4`
`"or " 2sqrt(2) le |x-y|+|x+y| le 4sqrt(2) " " (1)`
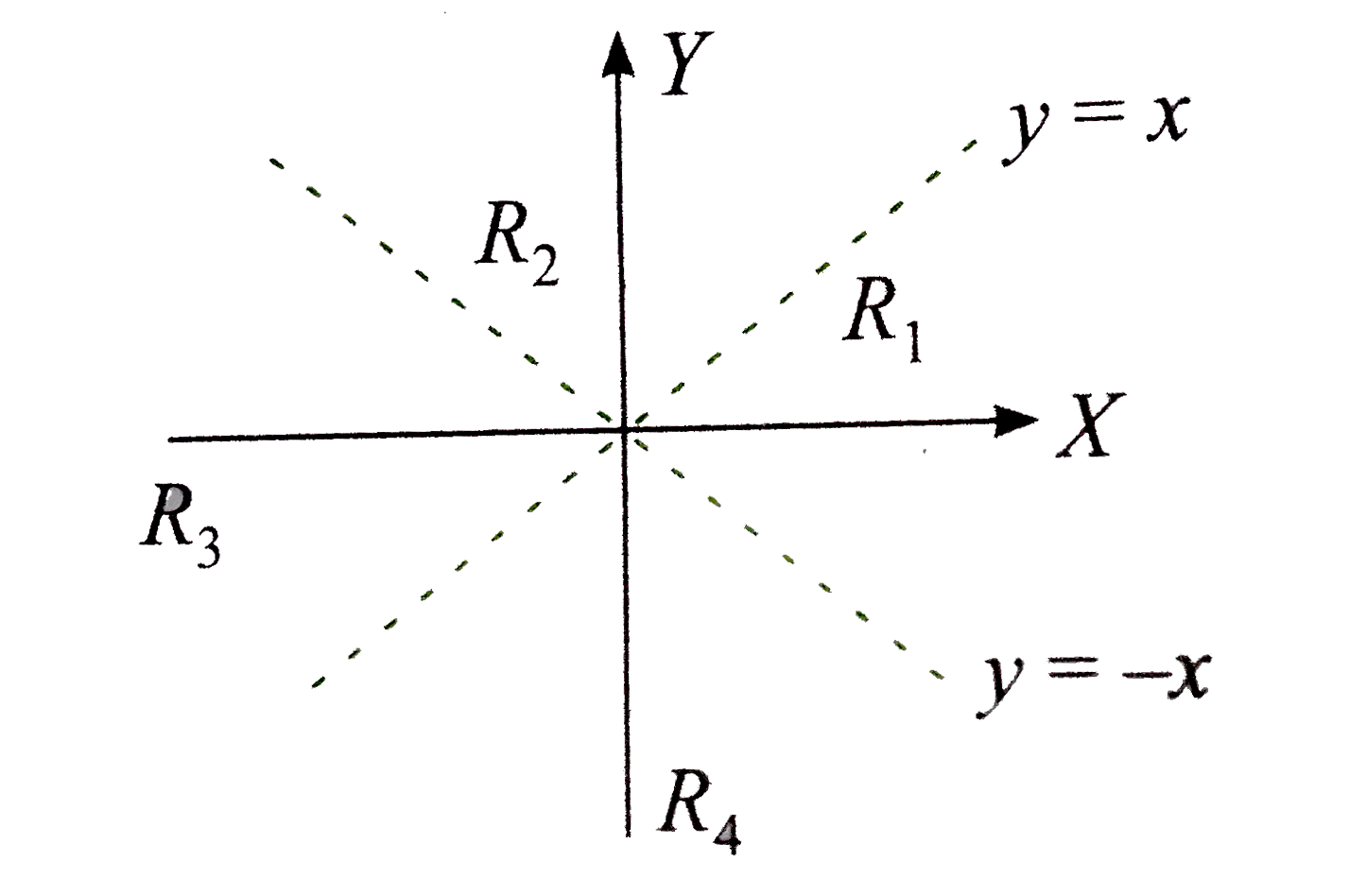
Now, let us consider the four regions, namely, `R_(1),R_(2), R_(3) " and " R_(4), " in the lines " L_(1) " and " L_(2)` dividing the coordinate plane.
`"In" R_(1)," we have " y lt x, y gt-x. "In " R_(2), " we have " y gt x, y gt -x. "Similarly,`
`"In" R_(3)," we have " y gt x, y lt-x. "Finally, in " R_(4), " we have " y lt x, y lt -x.`
Thus , for `R_(2),` (1) becomes.
`2sqrt(2) le x-y+x+y le 4sqrt(2) " or" sqrt(2) le x le 2sqrt(2)`
Similarly, for `R_(2)`, (1) becomes
`2sqrt(2) le y-x+x+y le 4sqrt(2) " or" sqrt(2) le y le 2sqrt(2)`
In `R_(3)` ,(1) will become
`2sqrt(2) le y-x-x-y le 4sqrt(2) " or" -sqrt(2) le x le -2sqrt(2)`
Finally, in `R_(4),` (1) will become
`2sqrt(2) le x-y-x-y le 4sqrt(2)`
`"or " -2sqrt(2) le y le -2sqrt(2)`
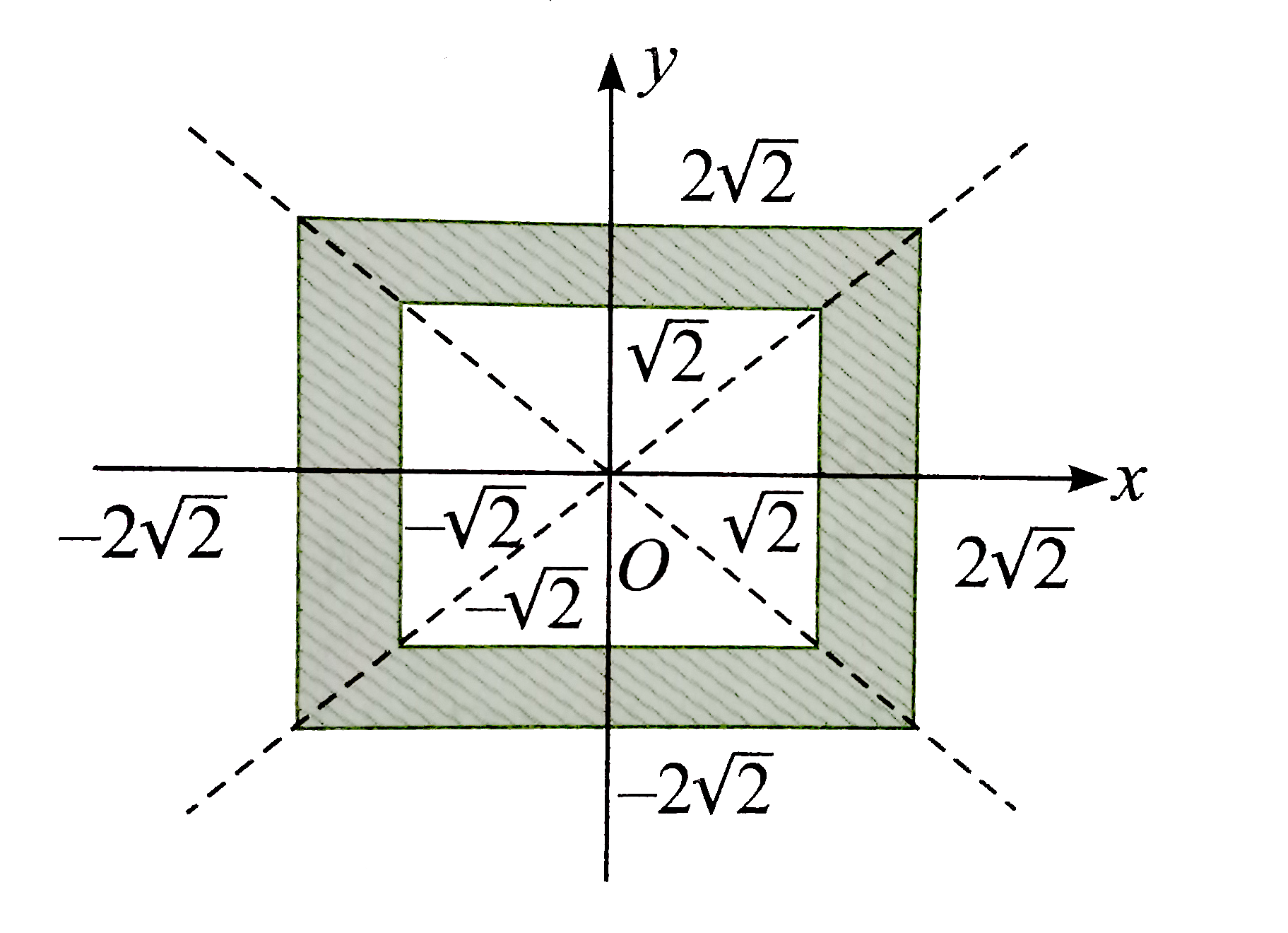
Thus region R will be the region between concentric squares formed by the lines `x=+-sqrt(2), y=+-sqrt(2) " and " x=+-2sqrt(2), y=+-2sqrt(2).`
Thus the required are is `(4sqrt(2))^(2)-(2sqrt(2))^(2) = 24` units.