`d(P, OA) le " min" [d(P,OB),d(P,AB)],`
`rArr d(P, OA) le d(P,OB) "and "d(P,OA) le d (P,AB),`
When d(P,OA)= d(P,OB), P is equidistant from OA and OB, i.e., P lies on angle bisector of lines OA and OB.
So, when `d(P, OA) lt d(P,OB)`, Point P is nearer to OA than to OB, i.e., it lies below bisector of OA and oB.
Similarly, when `d(P, OA) lt d(P,AB)` P is nearer to OA than to AB, i.e., it lies below bisector of OA and AB.
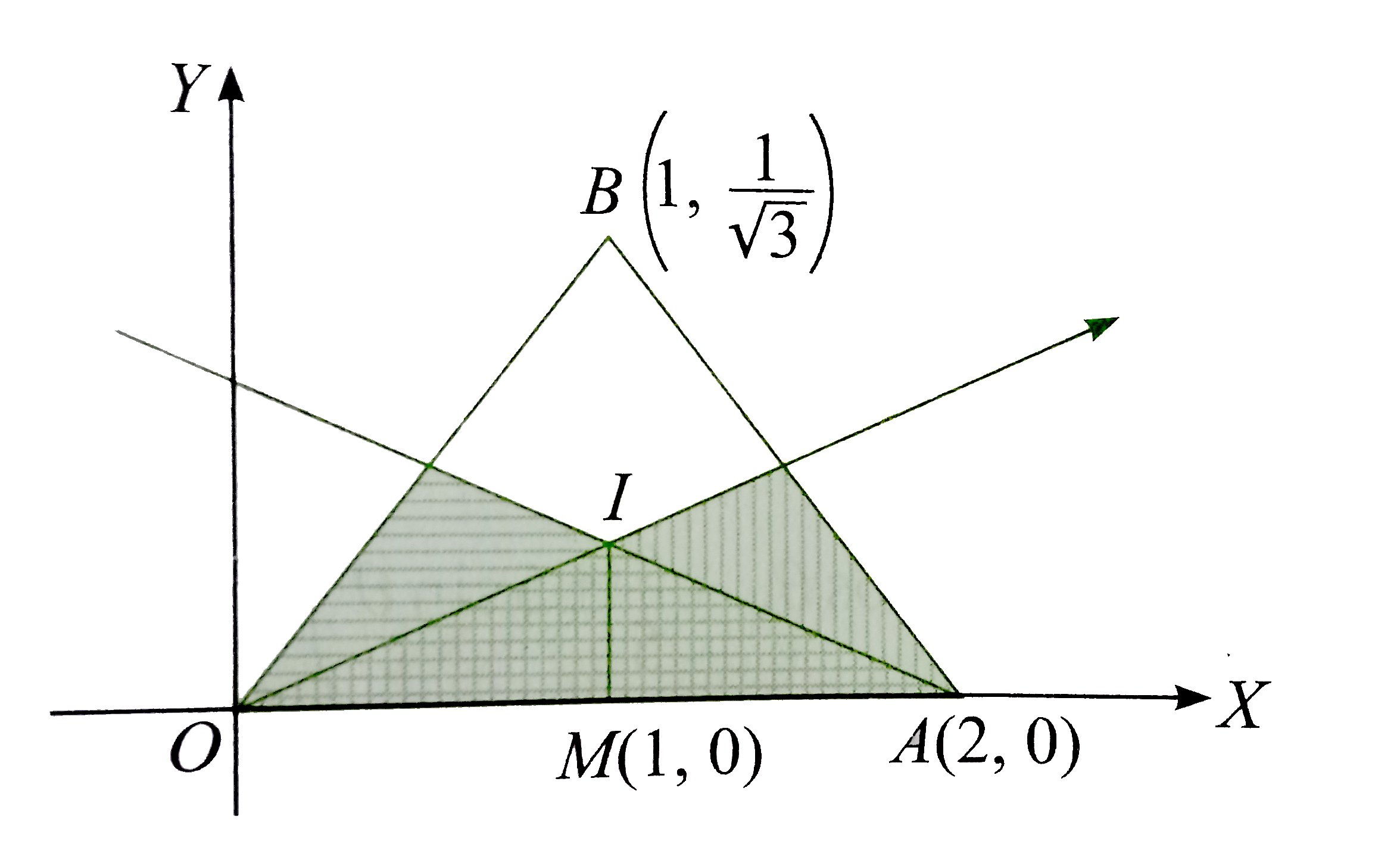
Common region satisfied by these two inequalities is the region formed by two bisectors and OA, i.e., triangle OIA.
`therefore " Required area " =" Area of triangle OIA"`
`"Now, " angle BOA = (1//sqrt(3))/(1) = (1)/(sqrt(3))`
`therefore angle BOA = 30^(@)`
`rArr angle IOA = 15^(@)`
`rArr IM ="tan" 15^(@) = 2-sqrt(3)`
`therefore "Area of triangle OIA" =(1)/(2) xx OA xx IM`
` =(1)/(2) xx 2 xx (2-sqrt(3)) = 2-sqrt(3) " sq. units" `