For P(x, y), we have
`2 le d_(1)(P) +d_(2)(P) le 4`
`rArr 2 le (|x-y|)/(sqrt(2)) + (|x+y|)/(sqrt(2)) le 4`
`2sqrt(2) le |x-y| +|x+y| le 4sqrt(2)`
In first quadrant, if `x gt y,` we have
`2sqrt(2) le x-y +x+y le 4sqrt(2)`
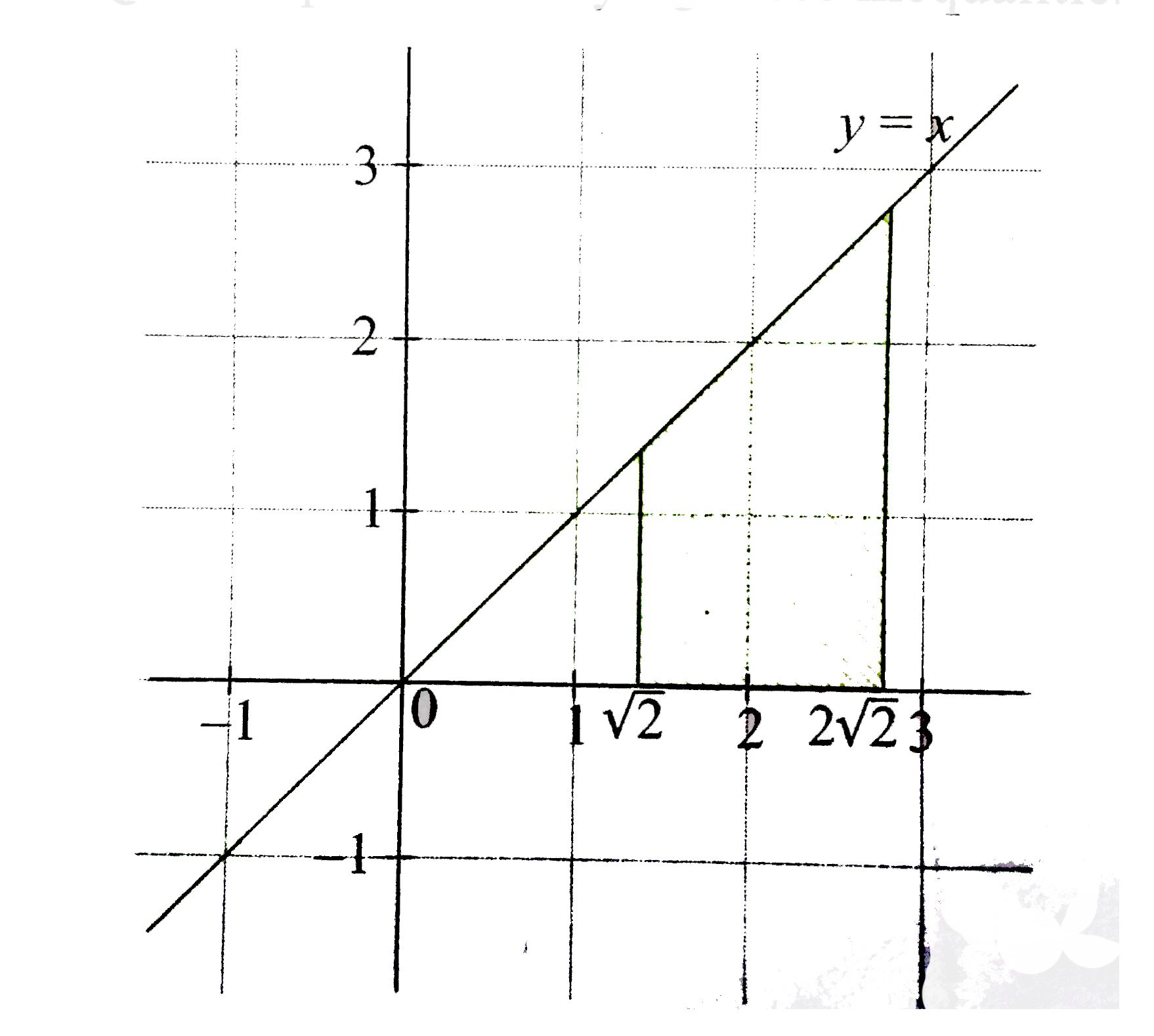
`"or " sqrt(2) le x le 2sqrt(2)`
The region of points satisfying these inequalities is
In first quadrant, if `x lt y`, we have
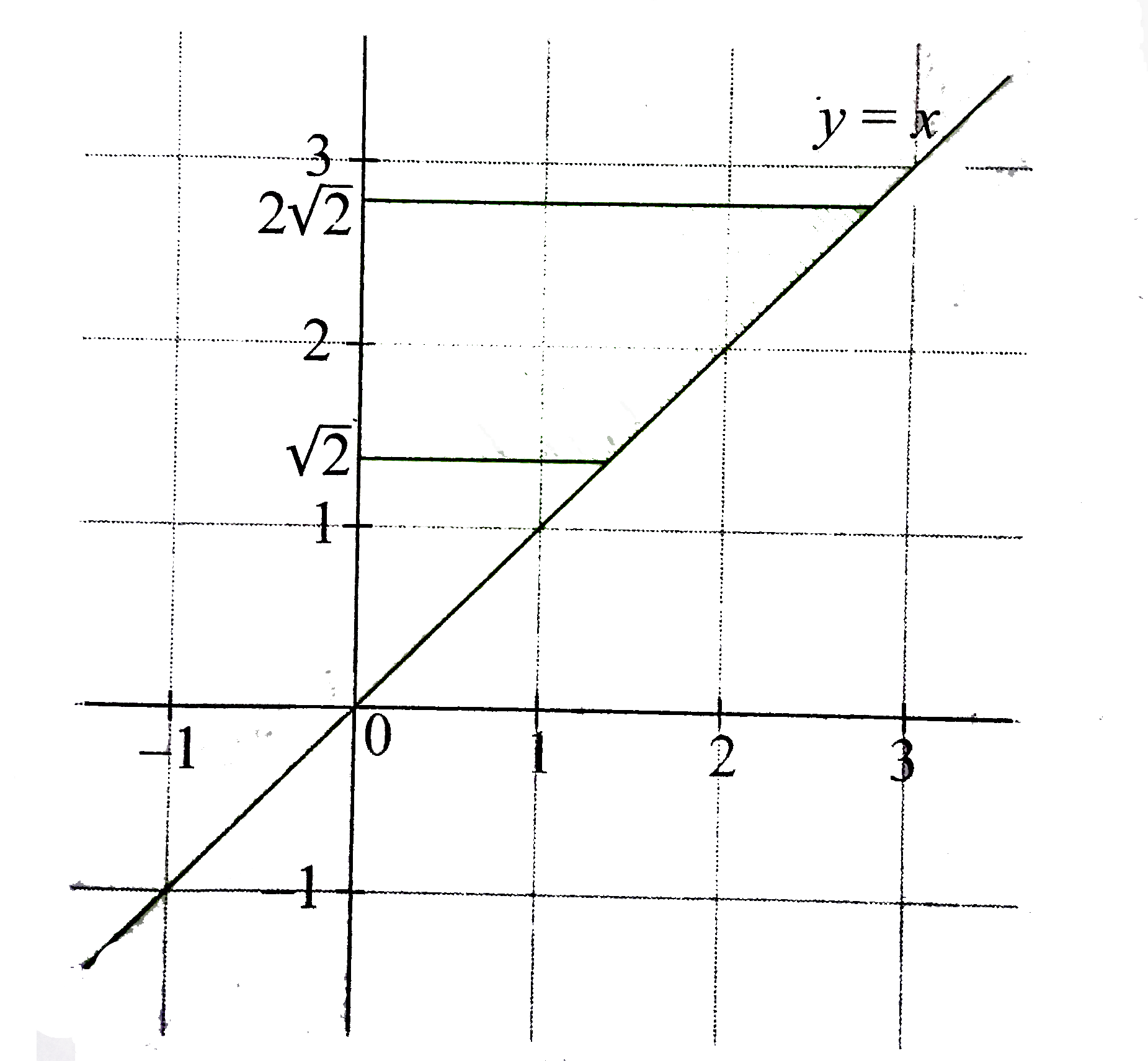
`"or " sqrt(2) le y le 2sqrt(2)`
The region of points satisfying these inequalities is
Combining above two regions, we have
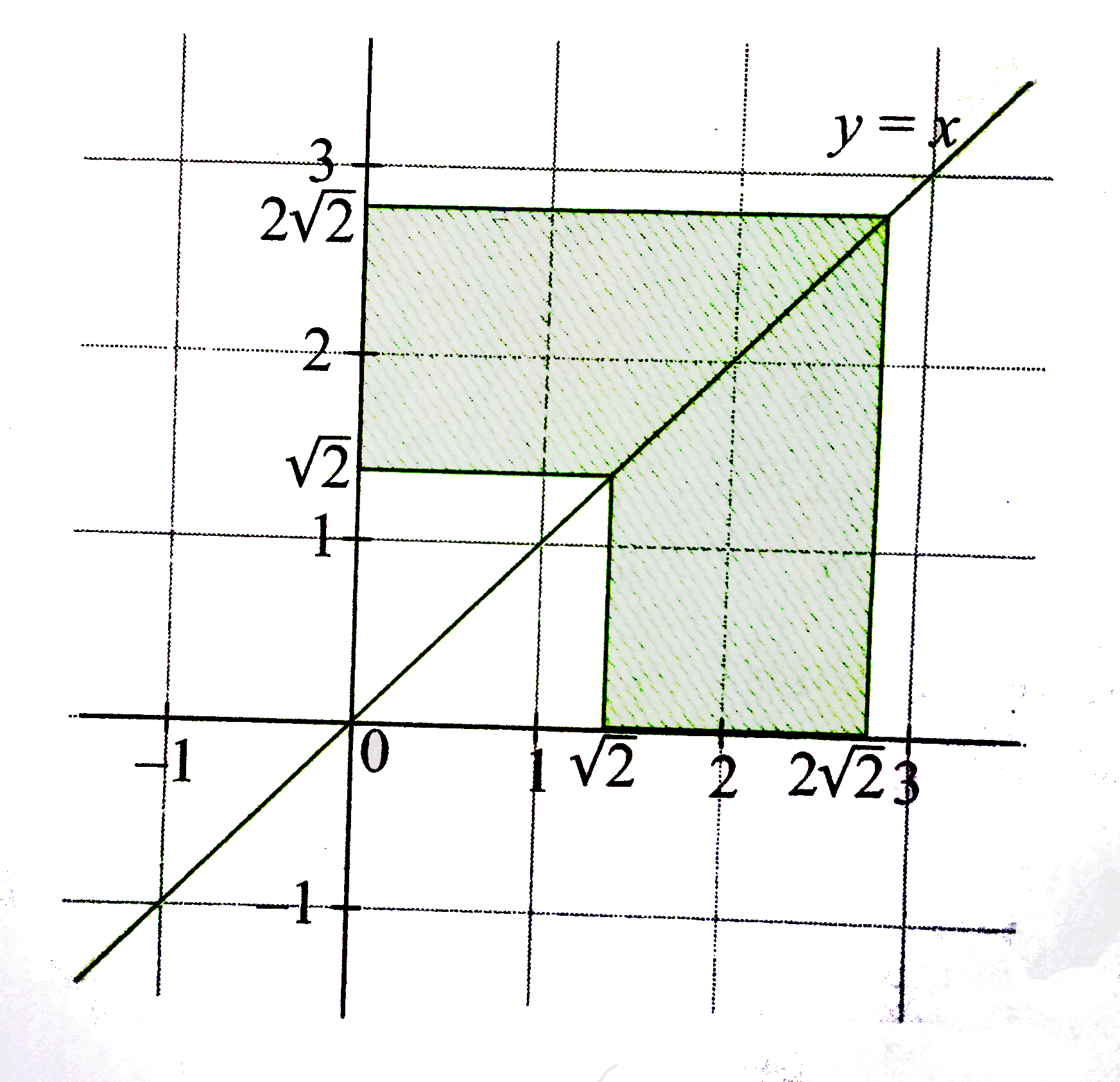
Area of shaded region `=((2sqrt(2))^(2) - (sqrt(2))^(2))`
=8-2= 6 sq. units