
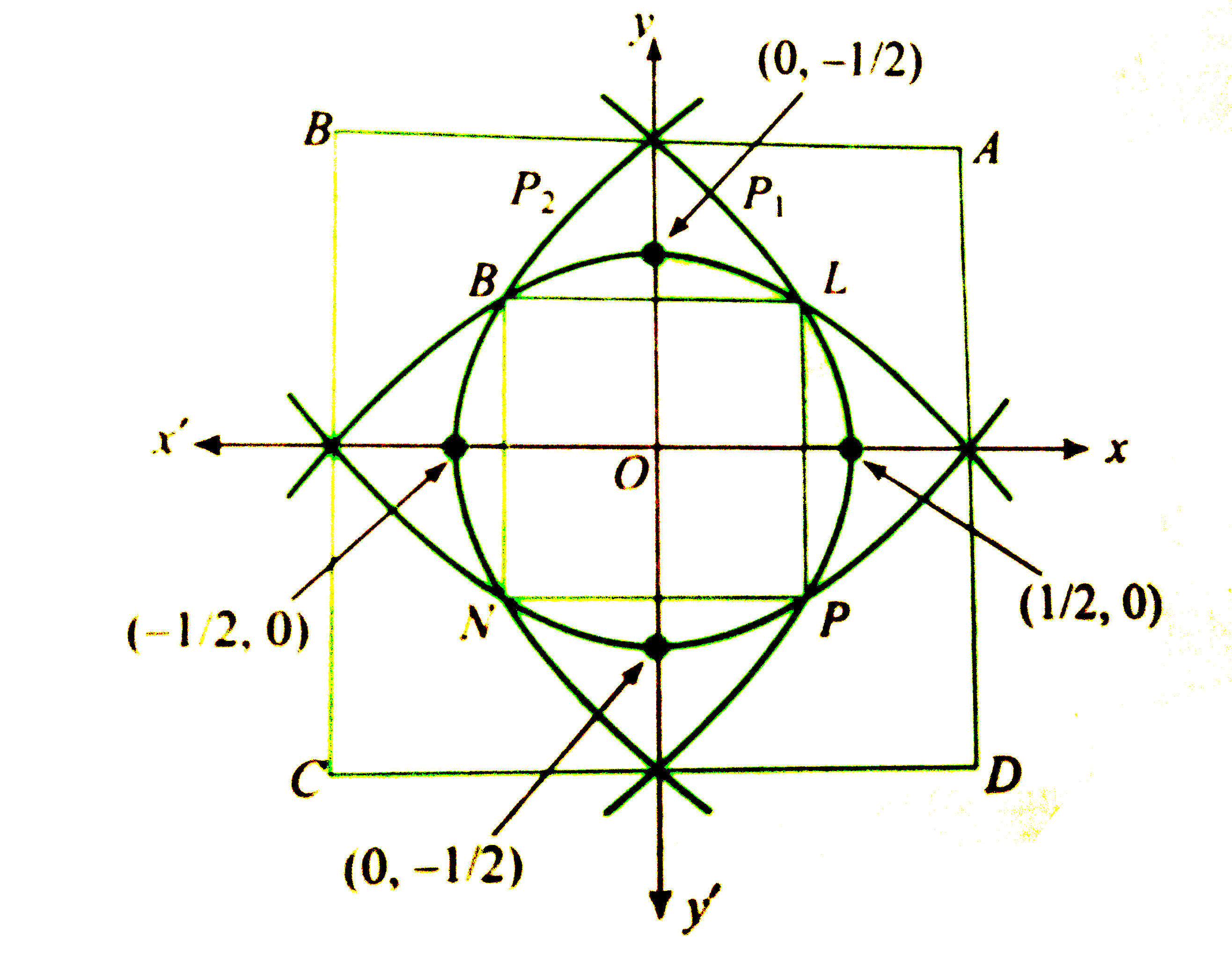
Let us consider any point (x,y) inside the square such that its distance from origin is less than its distance from any of the edges. Consider edge AD. Therefore,
`OPltPM`
`rArr" "sqrt((x^(2)+y^(2)))lt1 -x or y^(2)lt-2(x-(1)/(2))" (1)"`
Above represents all points within the parabola `y^(2)=1-2x`.
If we consider the edge BC, then `OPltPN` will imply
`y^(2)lt2(x+(1)/(2))" (2)"`
Similarly, if we consider the edges AB and CD, we will have
`x^(2)lt-2(y-(1)/(2))" (3)"`
`x^(2)lt2(y+(1)/(2))" (4)"`
Hence, S consists of the region bounded by four parabolas meeting
`"the axes at "(pm(1)/(2),0)and (0,pm(1)/(2))`
The point L is intersection of `P_(1) and P_(3)` given by (1) and (3).
Solving, we get
`y^(2)-x^(2)=-2(x-y)=2(y-x)`
`"or "y-x=0`
`"or "y=x`
`rArr" "x^(2)+2x-1=0`
`"or "(x+1)^(2)=2`
`"or "x=sqrt(2)-1" as x is + ve"`
`therefore" L is "(sqrt(2)-1,sqrt(2)-1).`
`therefore" Total area = "4["Square of side "(sqrt(2)-1)+2int_(sqrt(2)-1)^(1//2)sqrt(1-sqrt(2x))dx]`
`=4{(sqrt(2)-1)^(2)+2int_(sqrt(2)-1)^(1//2)sqrt((1-2x))dx}`
`=4[3-2sqrt(2)-(2)/(3){(1-2x)^(3//2)}_(sqrt(2)-1)^(1//2)]`
`=4[3-2sqrt(2)-(2)/(3){0-(1-2sqrt(2)+2)^(3//2)}]`
`=4[3-2sqrt(2)+(2)/(3)(3-2sqrt(2))^(3//2)]`
`=4(3-2sqrt(2))[1+(2)/(3)sqrt((3-2sqrt(2)))]`
`=4(3-2sqrt(2))[1+(2)/(3)(sqrt(2)-1)]`
`=(4)/(3)(3-2sqrt(2))(1+2sqrt(2))=(4)/(3)[(4sqrt(2)-5)]`
`=(16sqrt(2)-20)/(3)` sq. units.