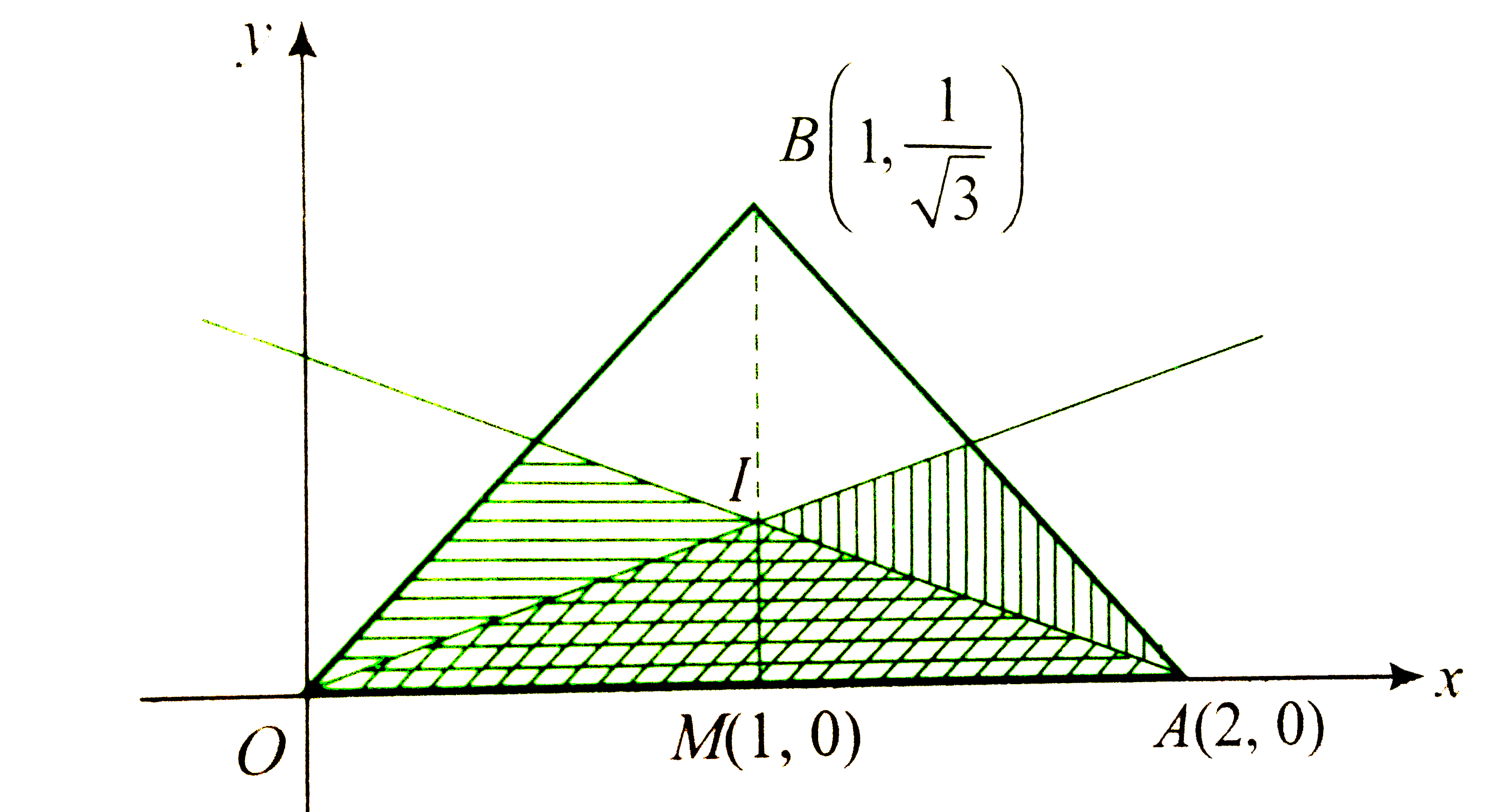
`d(P,OA)le" min "[d(P,OB), d(P,AB)]`
`rArr" "d(P,OA)le d(P,OB) and d(P,OA)led(P,AB)`
When `d(P,OA)=d(P,OB),P` is equidistant from OA and OB, or
P lies on the angular bisector of lines OA and OB.
Hence when `d(P,OA) le d(P,OB),` point P is nearer to OA than to
OB, i.e., lies on or below the bisector of OA and OB.
Similarly, when `d(P,OA)led(P,AB)`, P is nearer to OA then to OB, i.e., lies on or below the bisector of OA and AB.
`therefore" Required area = Area of "Delta OIA.`
`"Now, tan "angleBOA=(1//sqrt(3))/(1)=(1)/(sqrt(3))`
`"or "angleBOA=30^(@)rArrangleIOA=15^(@)`
`rArr" "IM=tan 15^(@)=2-sqrt(3).`
`"Hence, Area of "DeltaOIA =(1)/(2)OAxxIM=(1)/(2)xx2xx(2-sqrt(3))`
`2-sqrt(3)` sq. units.