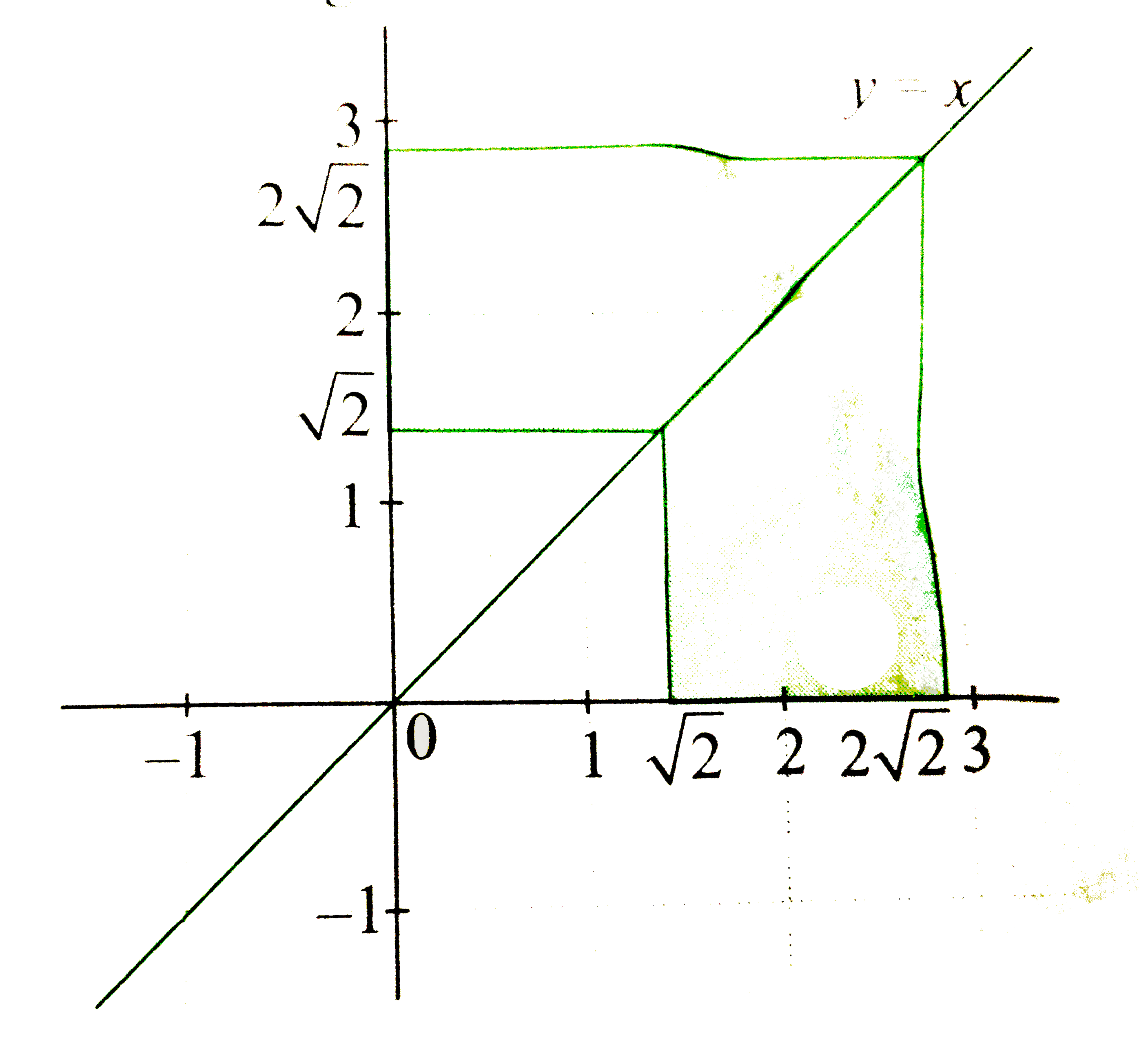
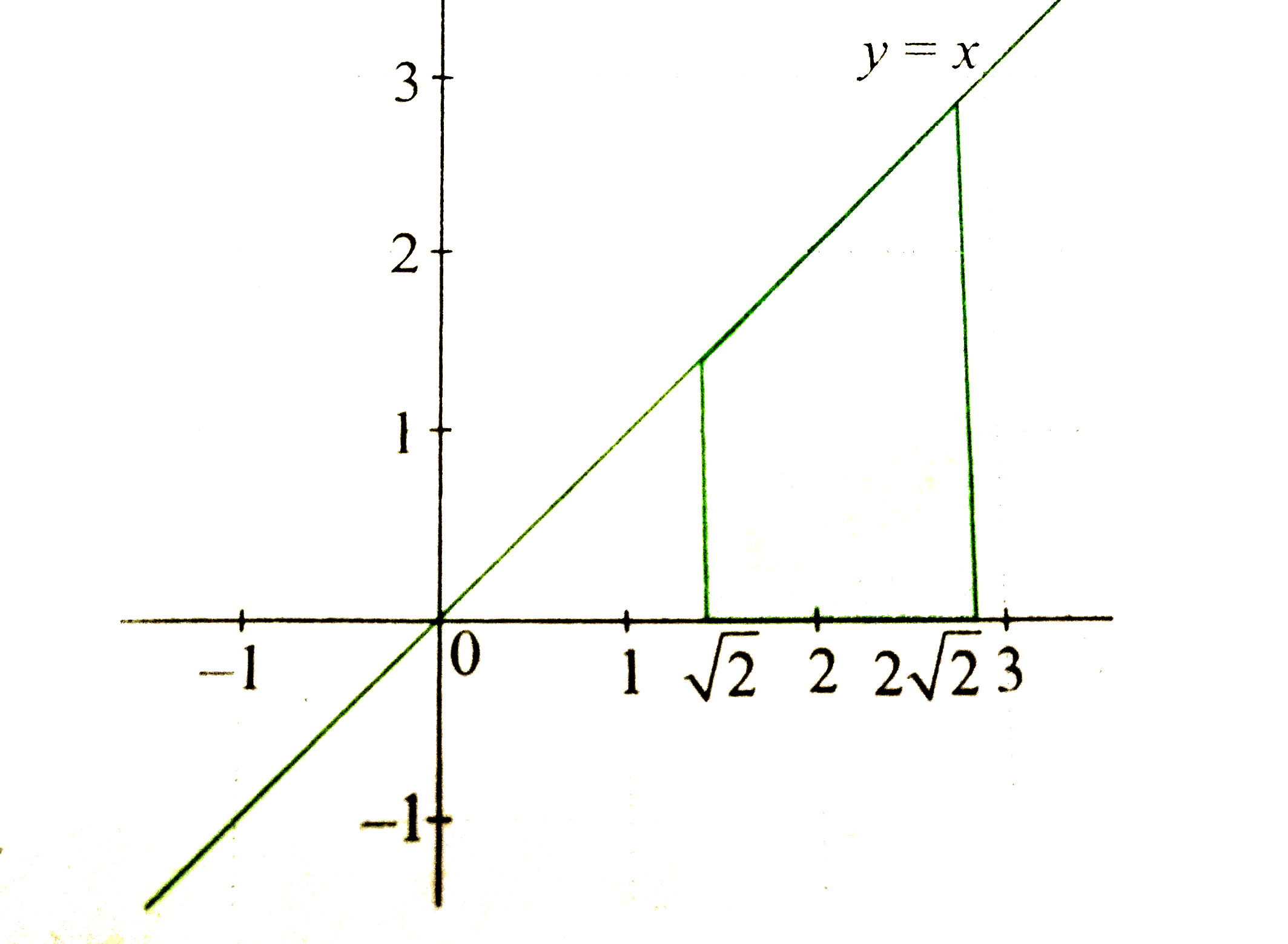
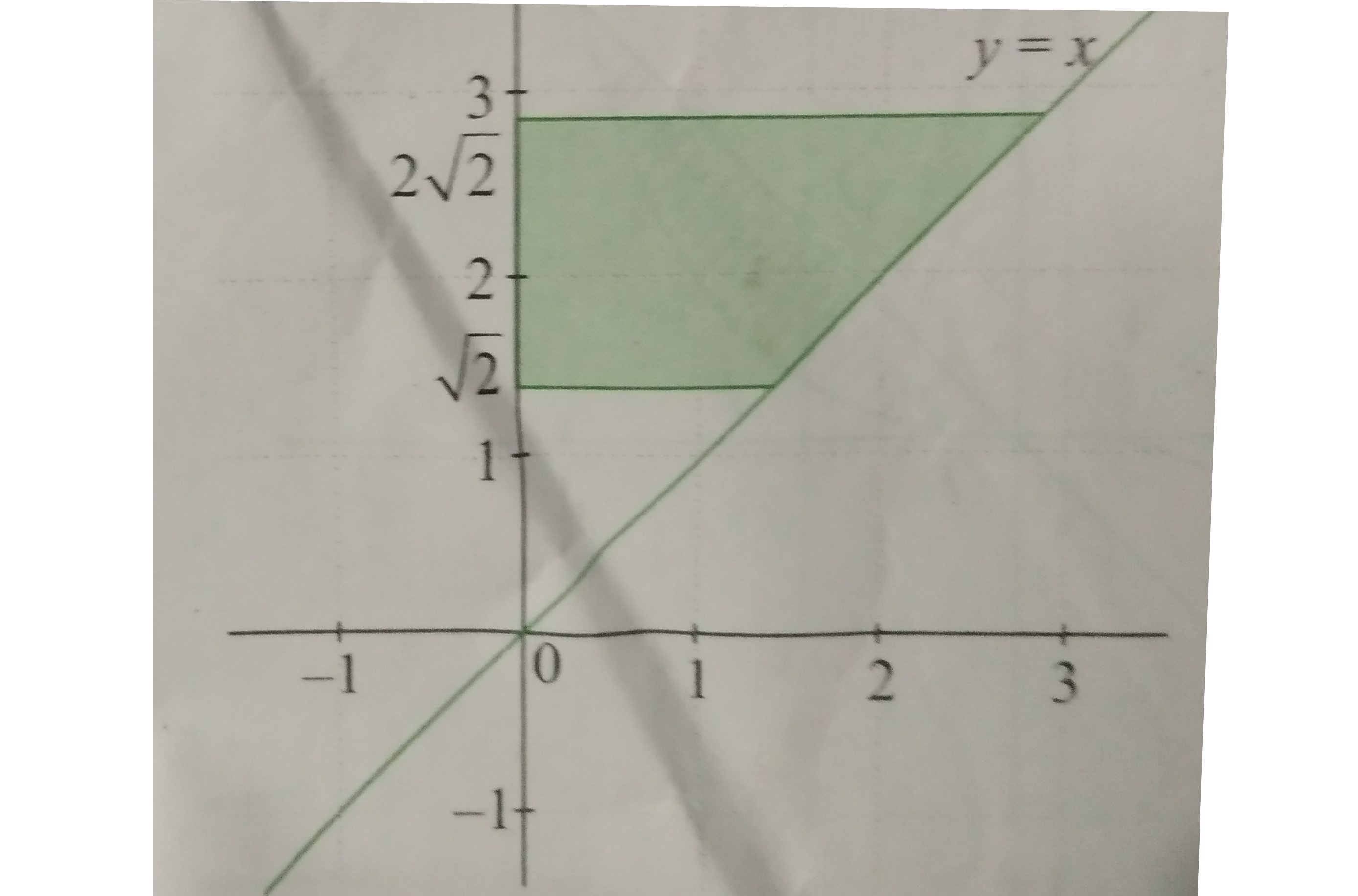
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-AREA-JEE Advanced Previous Year
- Find the area bounded by the curves x+2|y|=1 and x=0.
Text Solution
|
- The area bounded by the curve y=|cos^(-1)(sinx)|-|sin^(-1)(cosx)| and ...
Text Solution
|
- Area of the region {(x,y)inR^(2): y ge sqrt(|x+3|), 5ylex+9le15} is e...
Text Solution
|
- The area of the region bounded by the curve y=e^(x) and lines x=0 and ...
Text Solution
|
- The area of the region R={(x,y):|x| le|y| and x^2+y^2le1} is
Text Solution
|
- Let f:[0,oo)rarrR be a continuous function such that f(x)=1-2x+int(0)^...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that cosθ⋅cosecθ=cotθ
Text Solution
|
- For a point P in the plane, let d(1)(P) and d(2)(P) be the distances o...
Text Solution
|
- A farmer F1 has a land in the shape of a triangle with vertices at ...
Text Solution
|