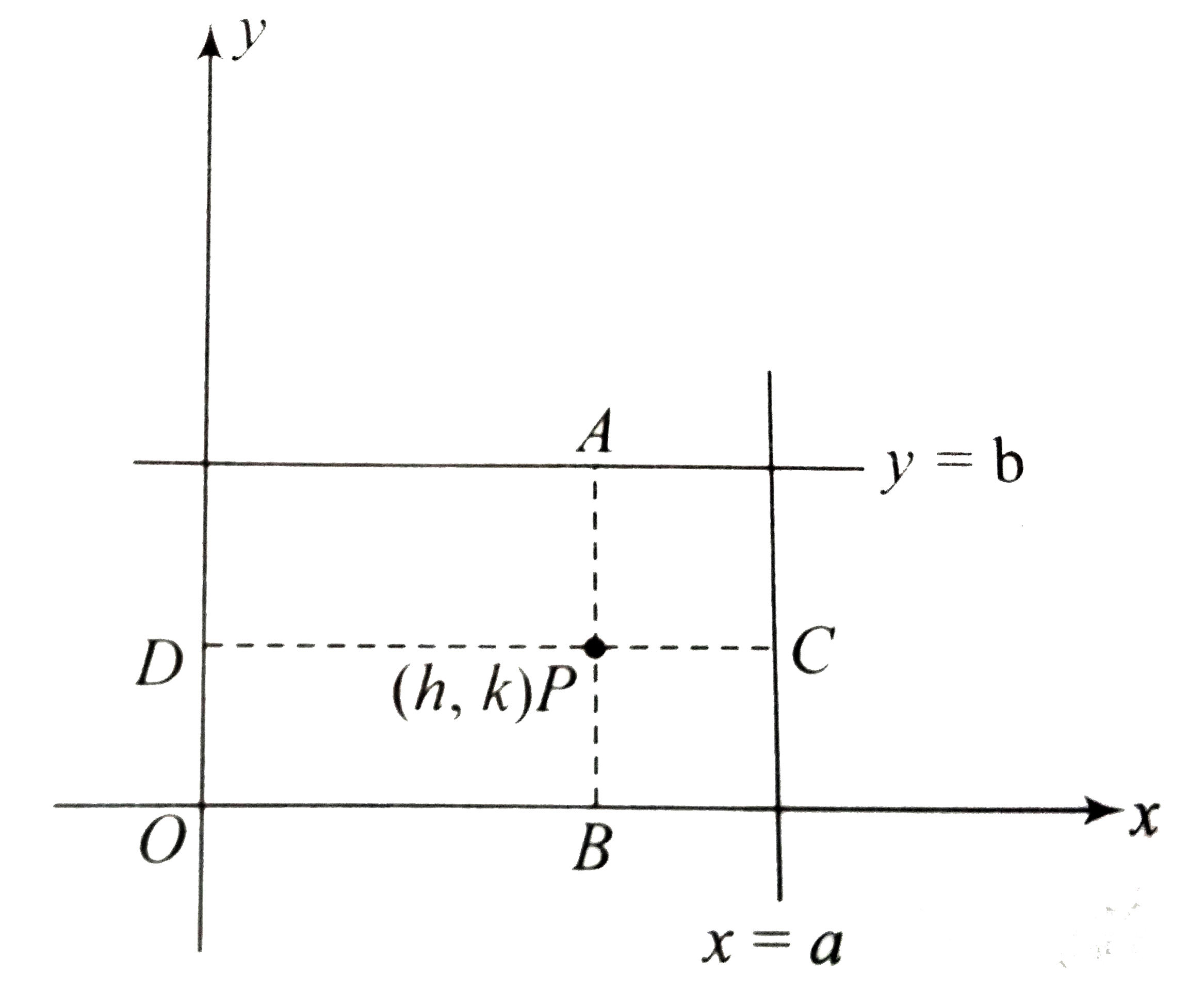
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A point moves such that the sum of the squares of its distances from t...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves so that the sum of the squares of its distances from ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the locus a point which moves in such a way that the sum of squar...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves such that the sum of the squares of its distances from t...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves such that the sum of the squares of its distances from t...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves such that the sum of the squares of its distances from t...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves such that the sum of the square of its distances from tw...
Text Solution
|
- A point movs in such a manner that the sum of the squares of its dista...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves so that the sum of squares of its distances from the poi...
Text Solution
|