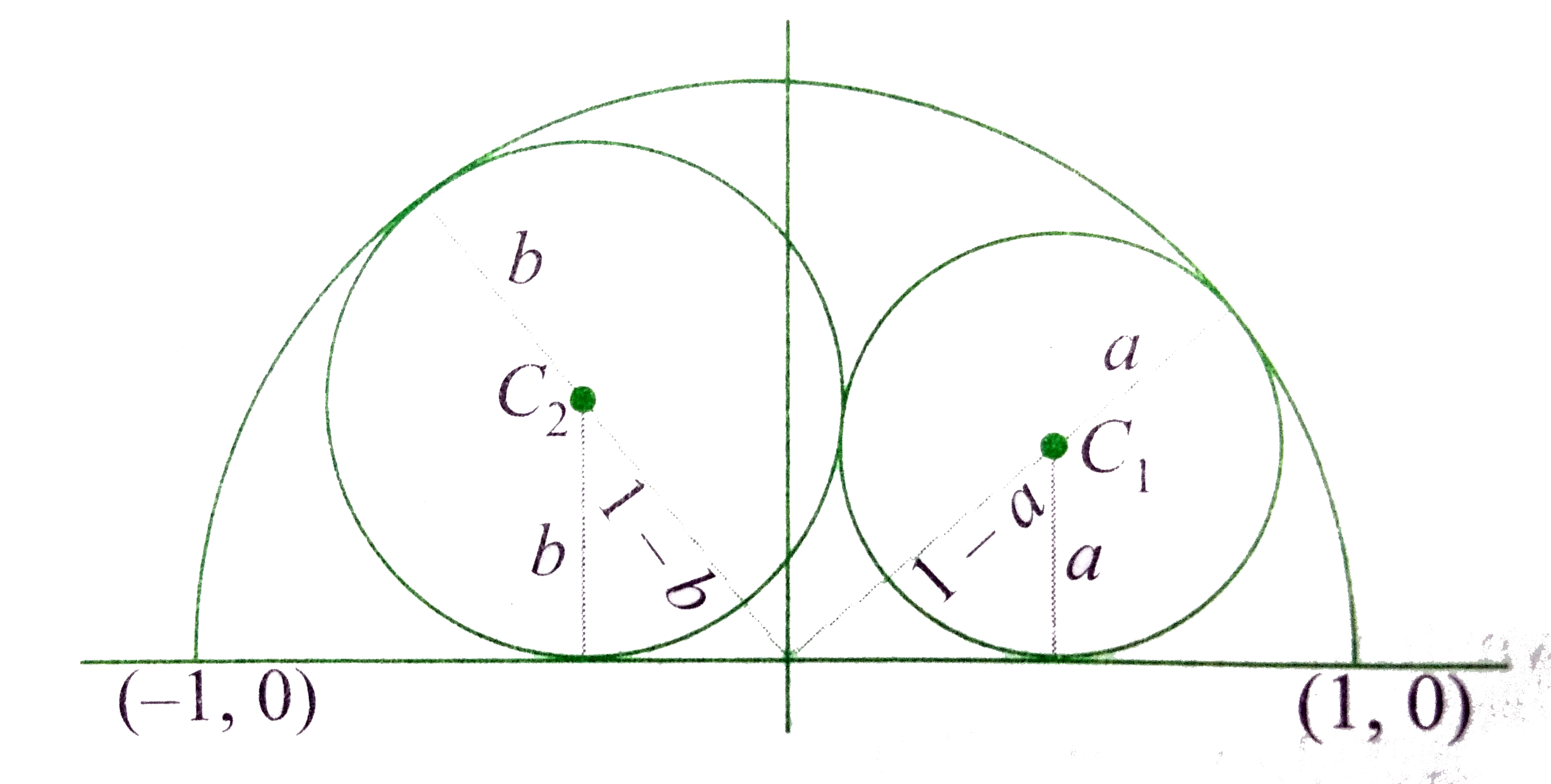A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-CIRCLE -Exercise (Single)
- A circle C1, of radius 2 touches both x-axis and y- axis. Another circ...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose a x+b y+c=0 , where a ,ba n dc are in A P be normal to a famil...
Text Solution
|
- Two circles of radii aa n db touching each other externally, are inscr...
Text Solution
|
- If the length of the common chord of two circles x^2+y^2+8x+1=0 and x^...
Text Solution
|
- If r1a n dr2 are the radii of the smallest and the largest circles, re...
Text Solution
|
- If C1: x^2+y^2=(3+2sqrt(2))^2 is a circle and P A and P B are a pair o...
Text Solution
|
- P is a point (a , b) in the first quadrant. If the two circles which p...
Text Solution
|
- Find the number of common tangent to the circles x^2+y^2+2x+8y-23=0 an...
Text Solution
|
- Find the locus of the centres of the circle which cut the circles x^2+...
Text Solution
|
- Tangent are drawn to the circle x^2+y^2=1 at the points where it is me...
Text Solution
|
- If the line xcostheta+ysintheta=2 is the equation of a transverse comm...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- The circles having radii r1a n dr2 intersect orthogonally. The length ...
Text Solution
|
- The two circles which pass through (0,a)a n d(0,-a) and touch the line...
Text Solution
|
- Locus of thews of the centre of the circle which touches x^2+y^2 - 6x-...
Text Solution
|
- If the chord of contact of tangents from a point P to a given circle p...
Text Solution
|
- If the angle of intersection of the circle x^2+y^2+x+y=0 and x^2+y^2+x...
Text Solution
|
- The coordinates of two points Pa n dQ are (x1,y1)a n d(x2,y2)a n dO is...
Text Solution
|
- If the circumference of the circle x^2 + y^2 + 8x + 8y - b = 0 is bise...
Text Solution
|
- Equation of the circle which cuts the circle x^2+y^2+2x+ 4y -4=0 and ...
Text Solution
|