A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
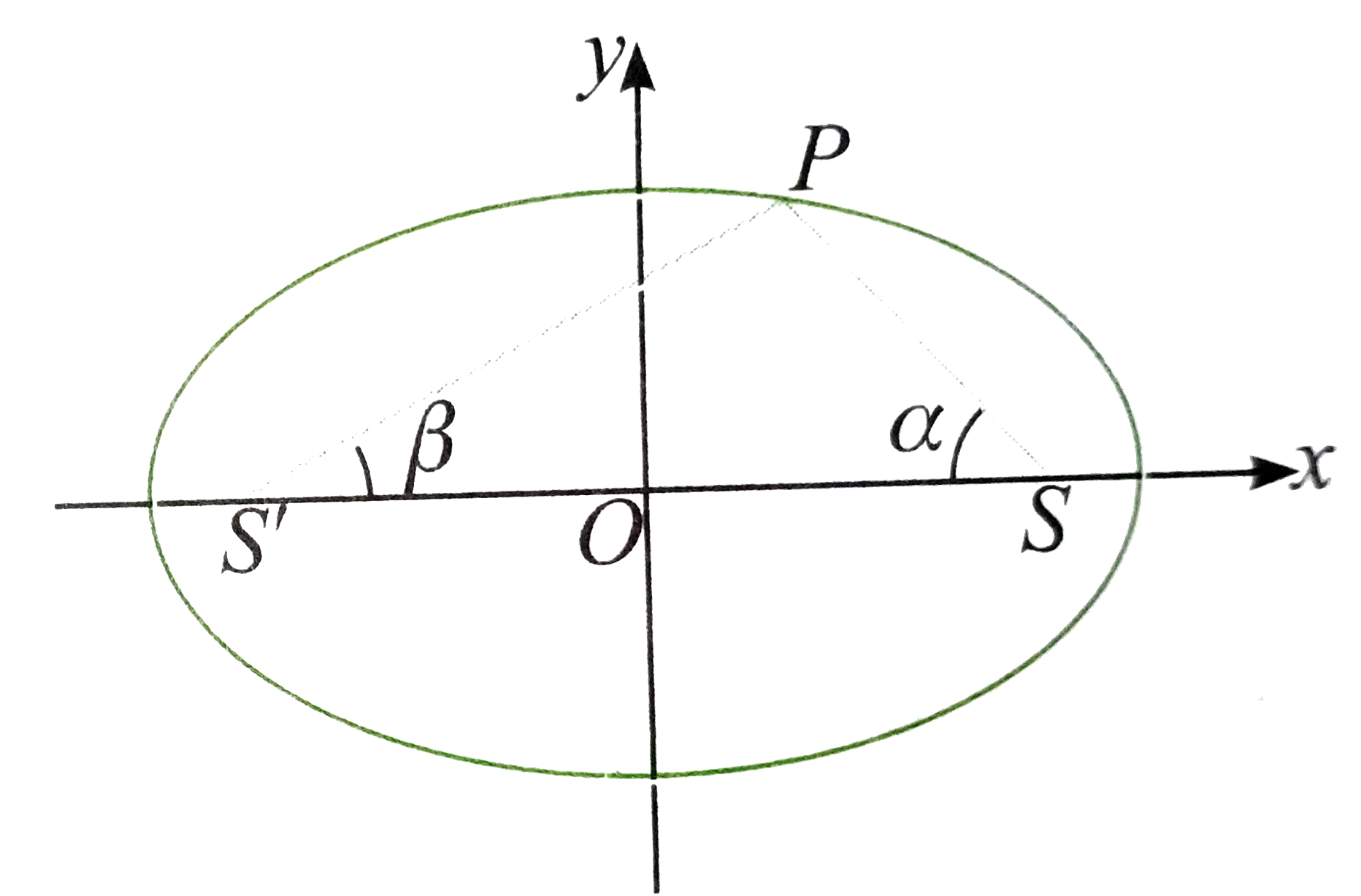
- P is any point lying on the ellipse (x^(2))/(a^(2))+(y^(2))/(b^(2))=1(...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha+beta+gamma=2pi, then (a) tan(alpha/2)+tan(beta/2)+tan(gamma...
Text Solution
|
- If P is any point lying on the ellipse x^2/a^2+y^2/b^2=1 , whose foci ...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha+beta+gamma=2pi, then (A) tan(alpha/2)+tan(beta/2)+tan(gamma/2...
Text Solution
|
- P is any point lying on the ellipse (x^(2))/(a^(2))+(y^(2))/(b^(2))=1(...
Text Solution
|
- If tan alpha =(1+2^(-x))^(-1) and tan beta =(1+2^(x+1))^(-1) then the...
Text Solution
|
- IF alpha , beta are eccentric angles of end points of a focal cho...
Text Solution
|
- tan (alpha + beta) =1/2, tan(alpha - beta) = 1/3 "then the value of" t...
Text Solution
|
- If tan theta = ( tan alpha + tan beta)/(1 + tan alpha tan beta),"show ...
Text Solution
|