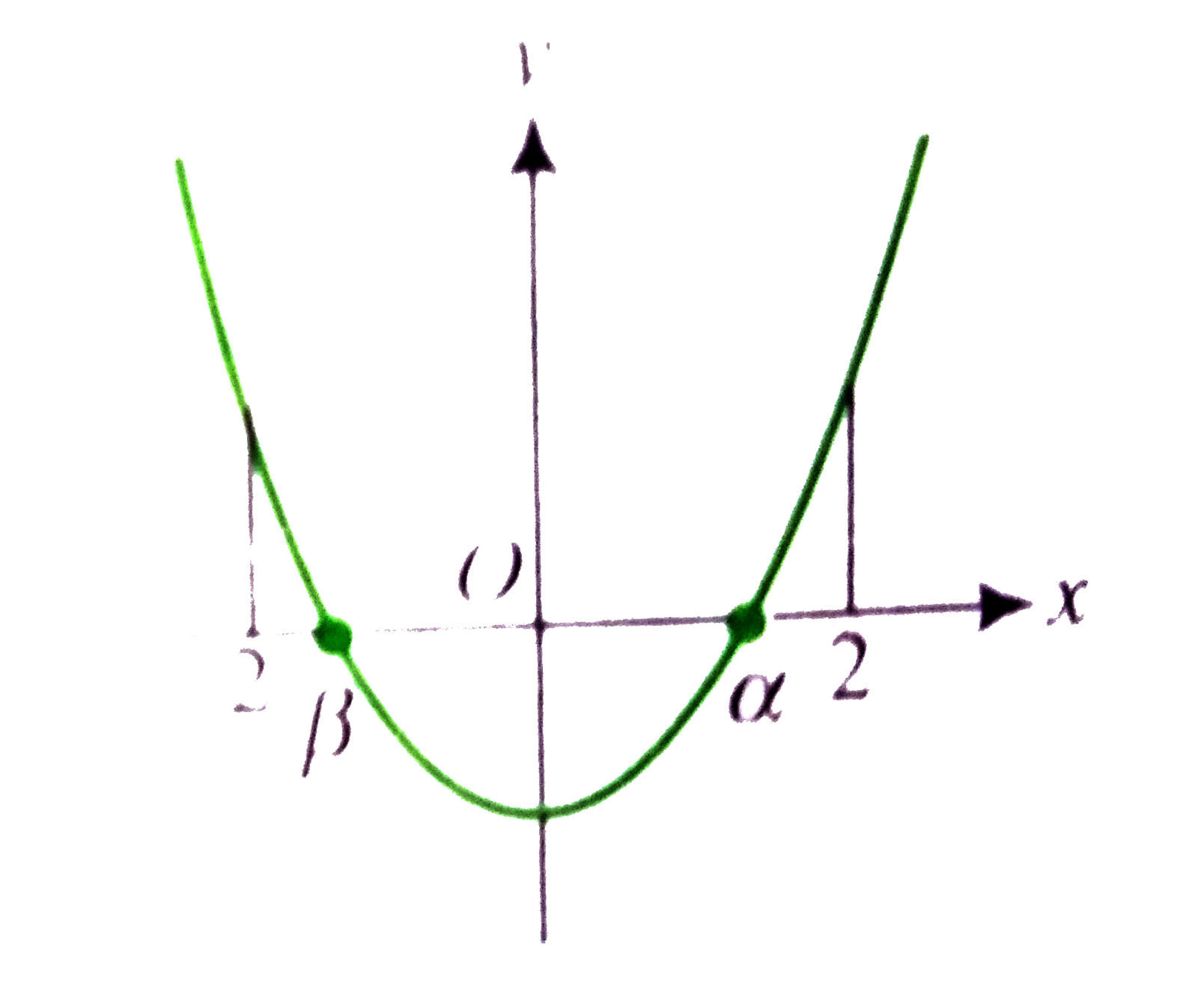
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE|Exercise Exercise (Comprehension)|37 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE|Exercise Exercise (Matrix)|6 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE|Exercise Exercise (Single)|89 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE|Exercise JEE Advanced Previous Year|4 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE|Exercise Question Bank|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-Exercise (Multiple)
- If (x^(2) + 5)/(2) = x - 2 cos (m + nx) has at least one real root, ...
Text Solution
|
- Let three quadratic equations ax^(2) - 2bx + c = 0, bx^(2) - 2 cx + a...
Text Solution
|
- For the quadratic equation x^2+2(a+1)x+9a-5=0, which of the following ...
Text Solution
|
- If a ,b ,c in Ra n da b c<0 , then equation b c x^2+2(b+c-a)x+a=0h a ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of the quadratic trinomial u=a x^2+b x+c has its vertex at (...
Text Solution
|
- Let a ,b ,c in Q^+ satisfying a > b > cdot Which of the following sta...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(X) = ax^(2) + bx + c . Consider the following diagram .
Text Solution
|
- Graph of y = ax^(2) + bx + c is as shown in the figure . If PQ= 9, ...
Text Solution
|
- ax^2 + bx + c = 0(a > 0), has two roots alpha and beta such alpha < -2...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation ax^(2) + bx + c = 0, a,b, c, in R have non -real ro...
Text Solution
|
- If cos x - y^(2) - sqrt(y - x ^(2) - 1 )ge 0 , then
Text Solution
|
- If a x^2+(b-c)x+a-b-c=0 has unequal real roots for all c in R ,t h e ...
Text Solution
|
- If (x^2+a x+3)//(x^2+x+a) takes all real values for possible real valu...
Text Solution
|
- If the range of function f(x) = (x + 1)/(k+x^(2)) contains the inter...
Text Solution
|
- Consider equation (x - sin alpha) (x-cos alpha) - 2 = 0 . Which of the...
Text Solution
|
- If the roots of the equation, x^3 + px^2+qx-1 = 0 form an increasing G...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a quadratic equation ax^2 + bx + c = 0 having roots alpha, b...
Text Solution
|
- The equaiton ((x)/(x+1))^(2) + ((x)/(x-1))^(2) = a(a-1) has
Text Solution
|
- lf the quadratic equations x^2+bx+c=0 and bx^2+cx+1=0 have a common r...
Text Solution
|
- If the inequality cot^(2)x + (k +1) cot x - (k-3) < 0 is true for at ...
Text Solution
|