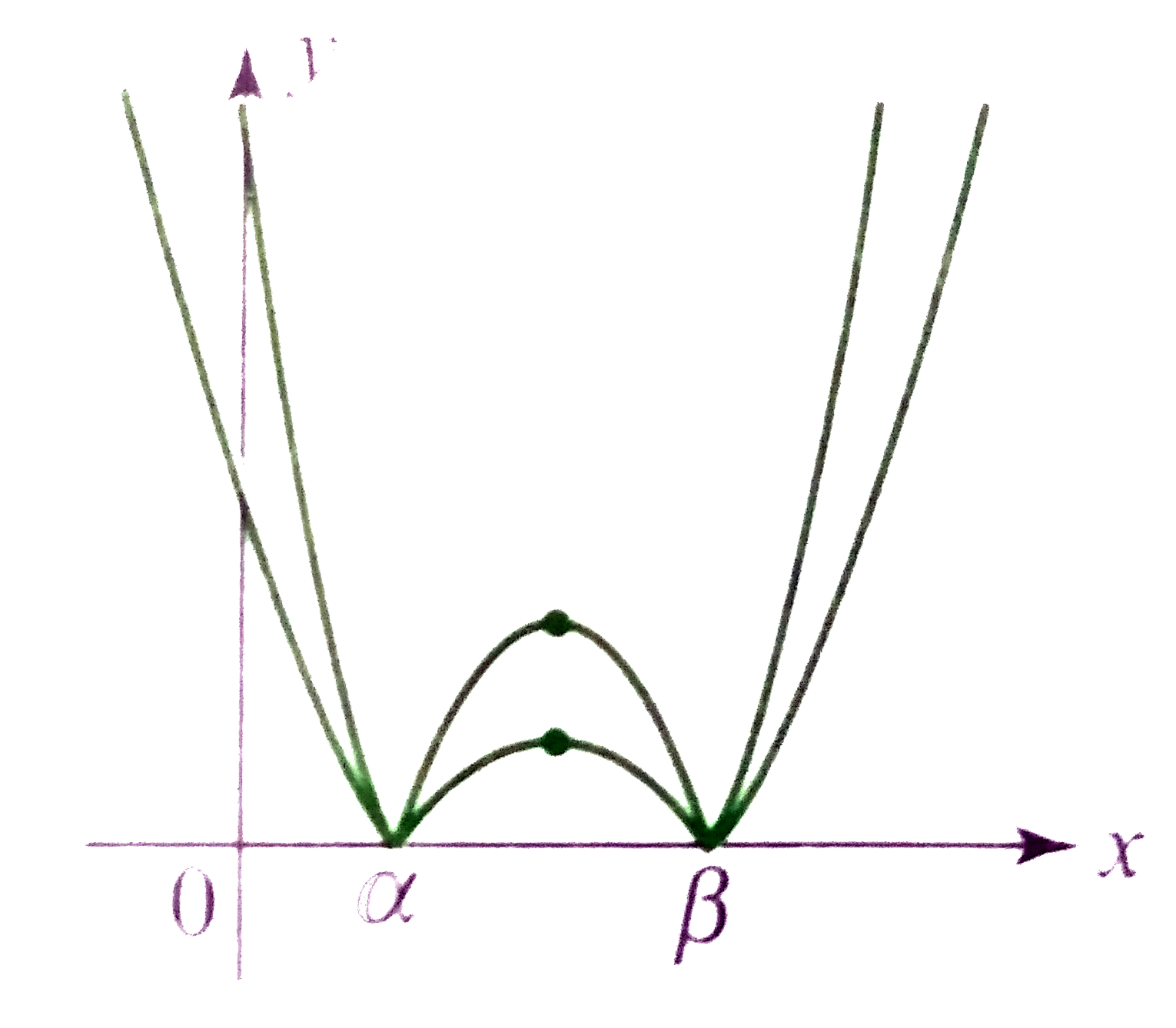
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE|Exercise Exercise (Matrix)|6 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE|Exercise Exercise (Numerical)|43 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE|Exercise Exercise (Multiple)|38 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE|Exercise JEE Advanced Previous Year|4 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE|Exercise Question Bank|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-Exercise (Comprehension)
- Consider the quadratic equation ax^(2) - bx + c =0,a,b,c in N which h...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation x^(2) + x + a - 9 lt 0 The values of the r...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation x^(2) + x + a - 9 lt 0 The values of the re...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation x^(2) + x + a - 9 lt 0 The value of the pa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation 9^(x) -a3^(x) - a+ 3 le 0, where a is real p...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation 9^(x) -a3^(x) - a+ 3 le 0, where a is real p...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation 9^(x) -a3^(x) - a+ 3 le 0, where a is real p...
Text Solution
|
- (af(mu) lt 0) is the necessary and sufficient condition for a particu...
Text Solution
|
- (af(mu) lt 0) is the necessary and sufficient condition for a particu...
Text Solution
|
- (af(mu) lt 0) is the necessary and sufficient condition for a particu...
Text Solution
|
- Given |px^(2) + qx + r| le |Px^(2) + Qx + r|AA x in R and d=q^(2) - 4...
Text Solution
|
- If (x+2) is a common factor of (px^2+qx+r) and (qx^2+px+r) then a) ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the slope of the following straight lines 4y-3=0
Text Solution
|
- Consider the equation x^4 + 2ax^3 + x^2 + 2ax + 1 = 0 where a in R. Al...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the equation x^4 + 2ax^3 + x^2 + 2ax + 1 = 0 where a in R. Al...
Text Solution
|
- The real numbers x1, x2, x3 satisfying the equation x^3-x^2+b x+gamma=...
Text Solution
|
- The real numbers x1, x2, x3 satisfying the equation x^3-x^2+b x+gamma=...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation x^4- λx^2+9=0 has four real and distinct roots, th...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation has no real root, then lamda lies in the interval
Text Solution
|
- If the equation x^4 -λx^2 +9 has only two real roods, then the set of ...
Text Solution
|