Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-CIRCLES-Question Bank
- If a x+b y=10 is the chord of minimum length of the circle (x-10)^2+(y...
Text Solution
|
- Locus of the poirit of intersection of the pair of perpendicular tange...
Text Solution
|
- Let A B and C D are two parallel chords of circle whose radius is 5 un...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- A straight line l1 with equation x-2y+10=0 meets the circle with equat...
Text Solution
|
- If the tangent at the point P on the circle x^2+y^2+6 x+6 y=2 meets th...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of the circle whose two normals are represented by the equa...
Text Solution
|
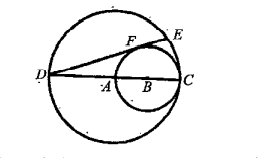
- If the diagram, D C is a diameter of the large circle centered at A, a...
Text Solution
|
- If 2 x-3 y=0 is the equation of the common chord of the circles, x^2+y...
Text Solution
|
- If one of the diameters of the circle x^2+y^2-2 x-6 y+6 =0 is a chord ...
Text Solution
|
- A circle touches the y-axis at the point (0, 4) and cuts the x-axis in...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given, two circles with centres Ct and C2 are 35 units a...
Text Solution
|
- If the lines 3x-4y+4=0 and 6x-8y-7=0 are tangents to a circle, then fi...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum distance of the point (4,4) from the circle x^2+y^2-2 x-...
Text Solution
|
- If the circle (x-a)^2+y^2=25 intersects the circle x^2+(y-b)^2=16 in s...
Text Solution
|
- If a circle S(x, y)=0 touches at the point (2,3) of the line x+y=5 and...
Text Solution
|
 .
.