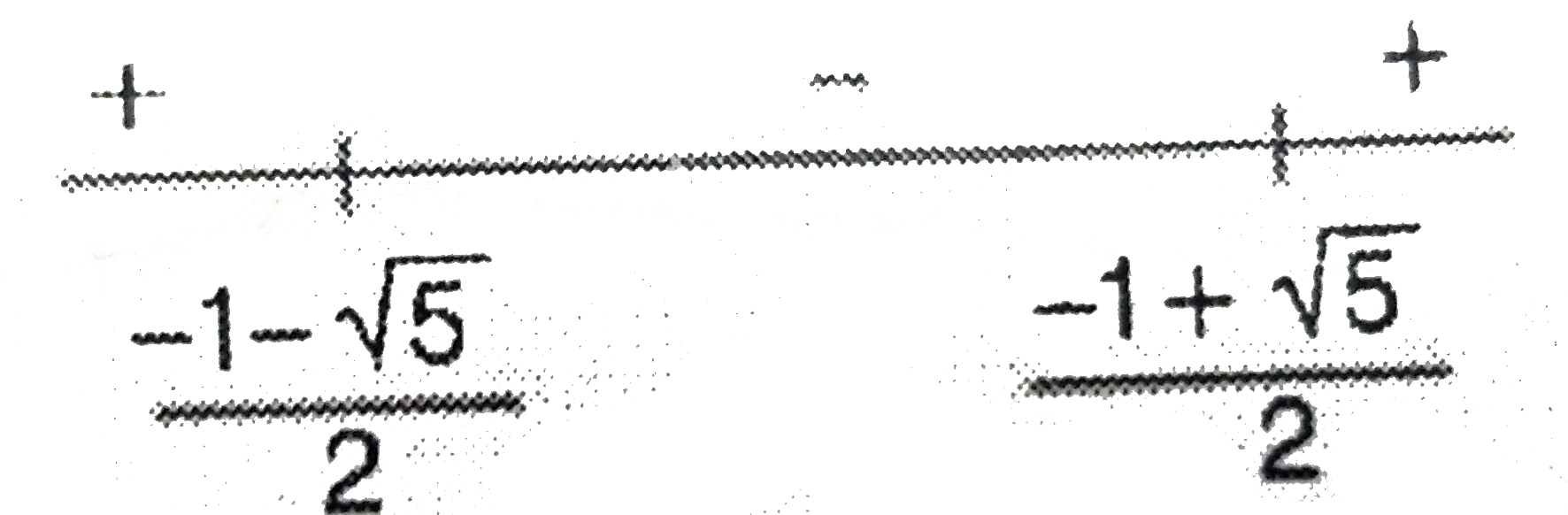A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- 5, 5r, 5r^2 are sides of a triangle. Which value of r cannot be possib...
Text Solution
|
- In triangle A B C , if cosA+cosB+cosC=7/4, t h e n R/r is equal to 3/4...
Text Solution
|
- If the sides of a triangle be in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4, the ratio of ...
Text Solution
|
- If 5, 5r and 5r^(2) are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, then r...
Text Solution
|
- यदि एक त्रिभुज की भुजाओ की लम्बाई 5, 5r, 5r^(2) है, तो r निम्न में से ...
Text Solution
|
- In triangle A B C , if cosA+cosB+cosC=7/4, t h e n R/r is equal to 3/4...
Text Solution
|
- If 5, 5r and 5r^(2) are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, then r...
Text Solution
|
- यदि एक त्रिभुज की भुजाओं की लम्बाई 5,5r,5r^(2) है, तो निम्न में से किस...
Text Solution
|
- If the length of the sides of a triangle 5,5r,5r^(2) Is, which of the ...
Text Solution
|