The equations of the sides of the square are as follow:
` AB: y=1, BC:x=-1, CD: y=-1, DA:x=1 `

Let the region be S and (x,y) is any point inside it.
Then, according to given conditions,
`sqrt(x^(2)+y^(2)) lt |1-x|, |1+x|,|1-y|,|1+y| `
` rArr x^(2)+y^(2) lt (1-x)^(2),(1+x)^(2),(1-y)^(2),(1+y)^(2) `
` rArr x^(2)+y^(2) lt x^(2)-2x+1, x^(2)+2x+1, y^(2)-2y+1, y^(2)+2y+1 `
`rArr y^(2) lt 1- 2x, y^(2) lt 1+2x, x^(2) lt 1-2y and x^(2) lt 2y +1 `
Now, in `y^(2)=1-2x " and " y^(2)=1+2x," ` the first equation represents a parabola with vertex at `(1//2,0)` and second equation represents a parabola with vertex `(-1//2,0)` and in ` x^(2)=1-2y " and " x^(2)=1+2y, ` the first equation represents a parabola with vertex at `(0,1//2)` and second equation represents a parabola with vertex at `(0,-1//2).` Therefore, the region S is lying inside the four parabolas
`y^(2)=1-2x,y^(2)=1+2x,x^(2)=1+2y, x^(2)=1-2y `
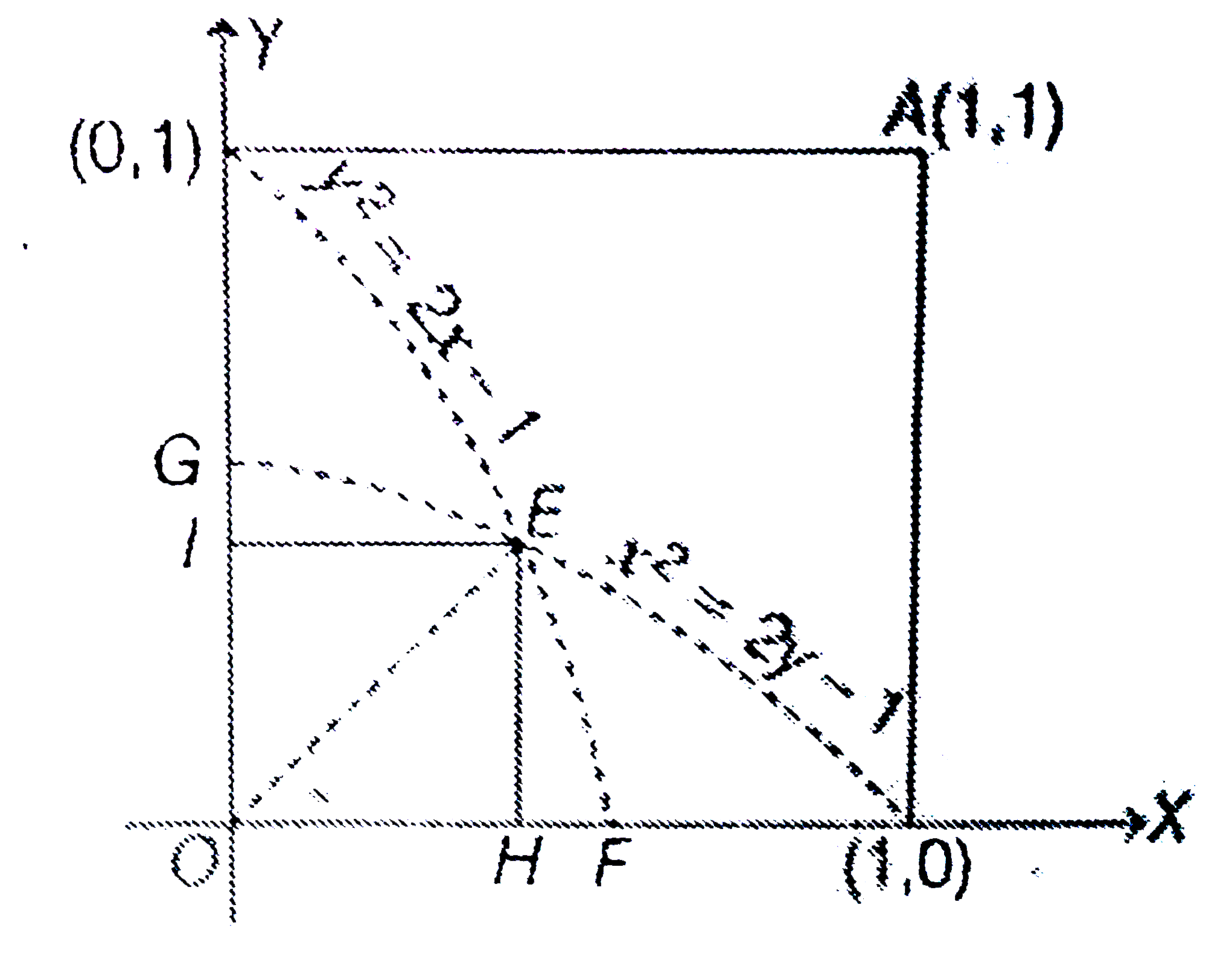
where, S in the shaded region.
Now, S in symmetrical in all four quadrants, therefore
`S=4 xx ` Area lying in the first quadrant.
Now, ` y^(2)=1-2x " and " x^(2)=1-2y ` intersect on the line ` y=x .` The point of intersection in `E(sqrt(2)-1, sqrt(2)-1).`
Area of the region OEFO
`=" Area of " triangle OEH + " Area of HEFH " `
` =(1)/(2)(sqrt(2)-1)^(2)+int_(sqrt(2)-1)^(1//2)sqrt(1-2x)dx `
`= (1)/(2)(sqrt(2)-1)^(2) + [(1-2x)^(3//2)(2)/(3)*(1)/(2)(-1)]_(sqrt(2)-1)^(1//2) `
` =(1)/(2)(2+1-2sqrt(2))+(1)/(3)(1+2-2sqrt(2))^(3//2)`
`=(1)/(2)(3-2sqrt(2))+(1)/(3)(3-2sqrt(2))^(3//2) `
`=(1)/(2)(3-2sqrt(2))+(1)/(3)[(sqrt(2)-1)^(2)]^(3//2) `
`=(1)/(2)(3-2sqrt(2))+(1)/(3)(sqrt(2)-1)^(3) `
` =(1)/(2)(3-sqrt(2))+(1)/(3)[2sqrt(2)-1-3sqrt(2)(sqrt(2)-1)]`
`=(1)/(2)(3-2sqrt(2))+(1)/(3)[5sqrt(2)-7] `
`=(1)/(6)[9-6sqrt(2)+10sqrt(2)-14]=(1)/(6)[4sqrt(2)-5] ` sq units
Similarly, area OEGO `=(1)/(6)(4sqrt(2)-5) ` sq units
Therefore, area of S lying in first quadrant
`=(2)/(6)(4sqrt(2)-5)=(1)/(3) (4sqrt(2)-5) ` sq units
Hence,`S=(4)/(3)(4sqrt(2)-5)=(1)/(3)(16sqrt(2)-20)` sq units

