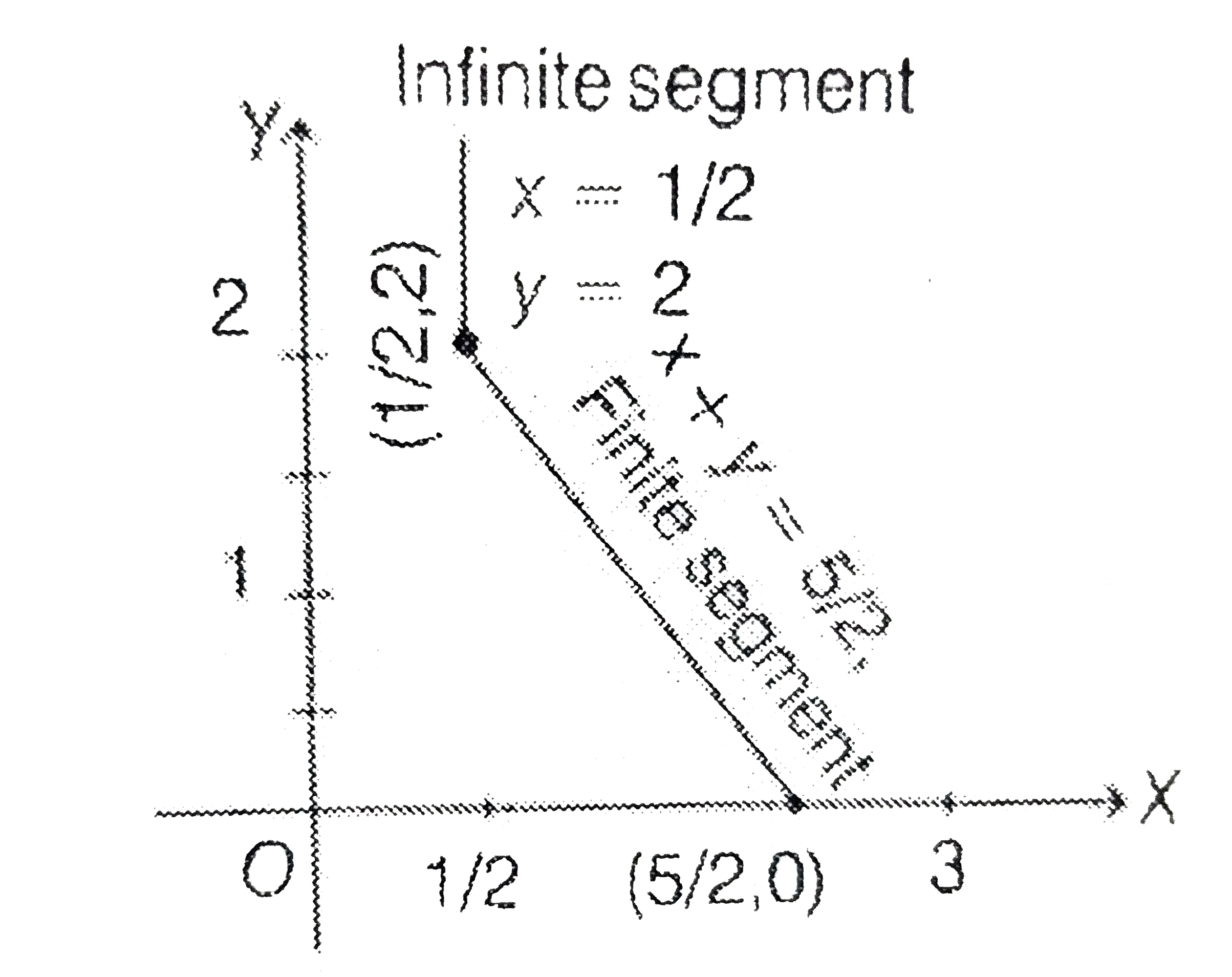
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For points P-=(x1, y1) and Q-=(x2, y2) of the coordinate plane, a new ...
Text Solution
|
- Let T(x,y), such that T is equidistant from point O and C with respect...
Text Solution
|
- For points P = (x1, y1) and Q = (x2,y2) of the coordinate plane, a new...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio in which the line segment joining P(x1,\ y1) and Q(x2,\ y...
Text Solution
|
- For points P-=(x1,y1) and Q-=(x2,y2) of the coordinates plane, a new d...
Text Solution
|
- For points P-=(x1,y1) and Q-=(x2,y2) of the coordinates plane, a new d...
Text Solution
|
- For points P-=(x1,y1) and Q-=(x2,y2) of the coordinates plane, a new d...
Text Solution
|
- For points P-=(x1, y1) and Q-=(x2, y2) of the coordinate plane, a new ...
Text Solution
|
- For points P-=(x1,y1) and Q-=(x2,y2) of the coordinates plane, a new d...
Text Solution
|