Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
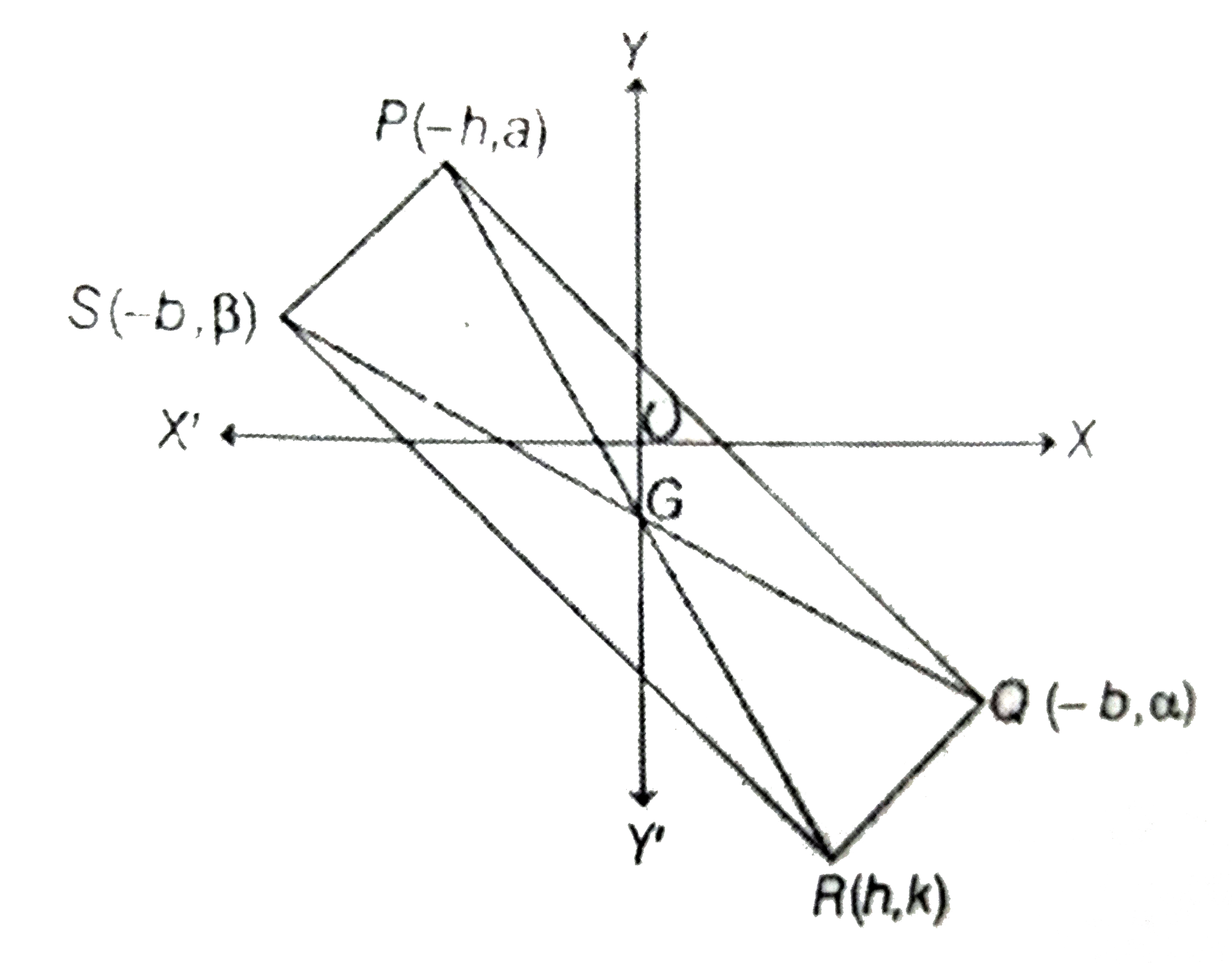
- A rectangle P Q R S has its side P Q parallel to the line y=m x and ve...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle PQRS has its side PQ parallel to the line y=mx and vertice...
Text Solution
|
- The lines (p-q)x+(q-r)y+(r-p)=0(q-r)x+(r-p)y+(p-q)=0,(x-p)x+(p-q)y+(q-...
Text Solution
|
- यदि |(a-b,b-c,c-a),(x-y,y-z,z-x),(p-q,q-r,r-p)|=m|(c,a,b),(z,x,y),(r,p...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle PQRS has its side PQ parallel to the line y = mx and verti...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle PQRS has its side PQ paralle to the line y=mx and vertices...
Text Solution
|
- आयत PQRS की भुजा PQ, रेखा y=mx के समान्तर है, तथा शीर्ष P, Q और ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle PQRS has its side PQ parallel to the line y= mx and verti...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle PQRS has its side PQ parallel to the line y= mx and verti...
Text Solution
|