Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
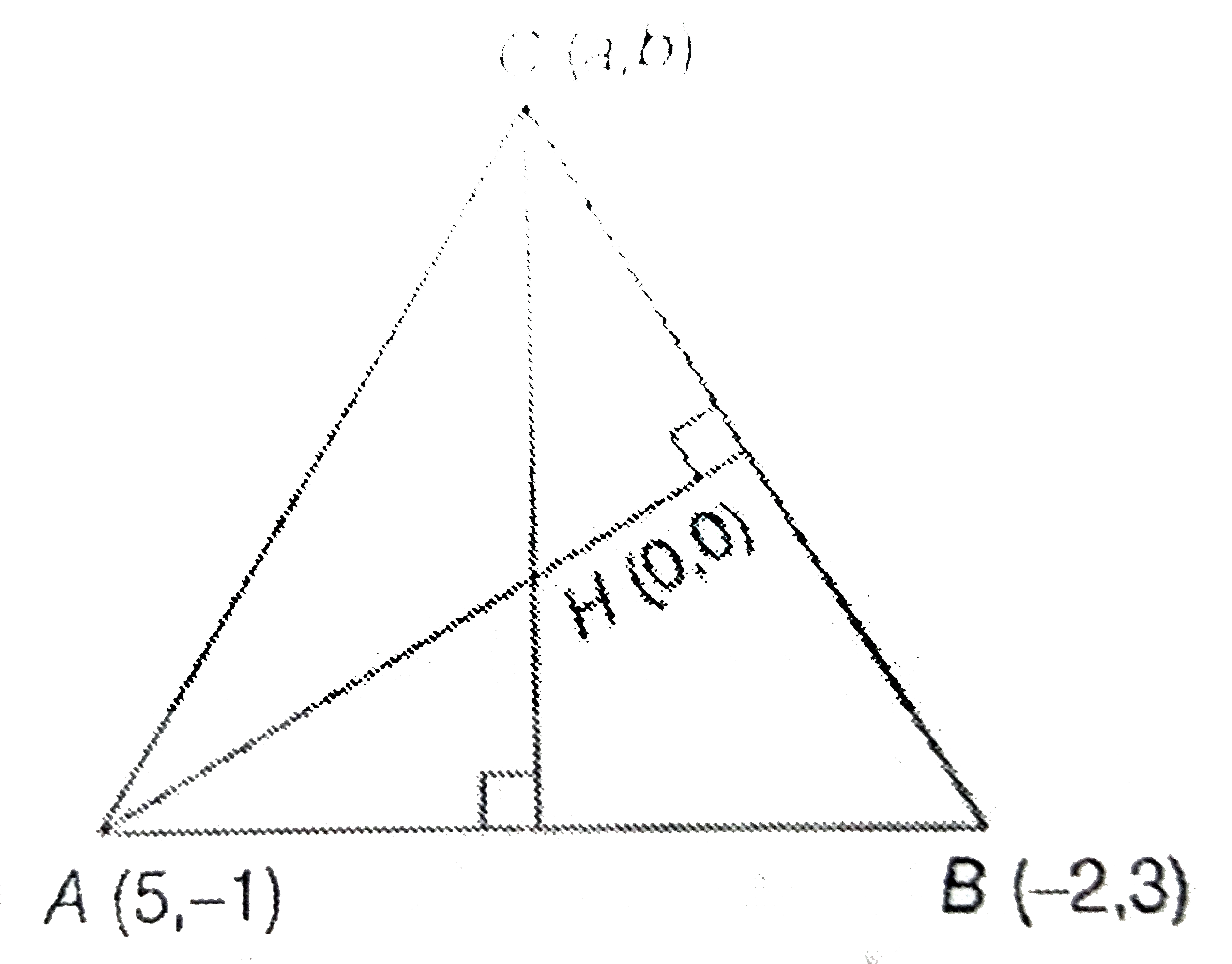
- Two vertices of a triangle are (5,-1) and (-2,3) If the orthocentre of...
Text Solution
|
- Two vertices of a triangle are (3,-1) and (-2,3) and its orthocenter ...
Text Solution
|
- Two vertices of a triangle are (5,-1) and (-2,3) If the orthocentre of...
Text Solution
|
- Two vertices of a triangle are (5,-1) and (-2,3). If the orthocentre o...
Text Solution
|
- यदि एक त्रिभुज के दो शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (1, 2), (3, 5) हैं तथा ...
Text Solution
|
- The coordinates of two vertices of a triangle are (-2,3) and (5,-1) ....
Text Solution
|
- Two vertices of a triangle are (5,-1) and (-2,3). If the orthocentre ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the coordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle whose vertices...
Text Solution
|
- Two vertices of a triangle ABC are B(5,-1) and C(-2,3) .If the orthoce...
Text Solution
|