A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
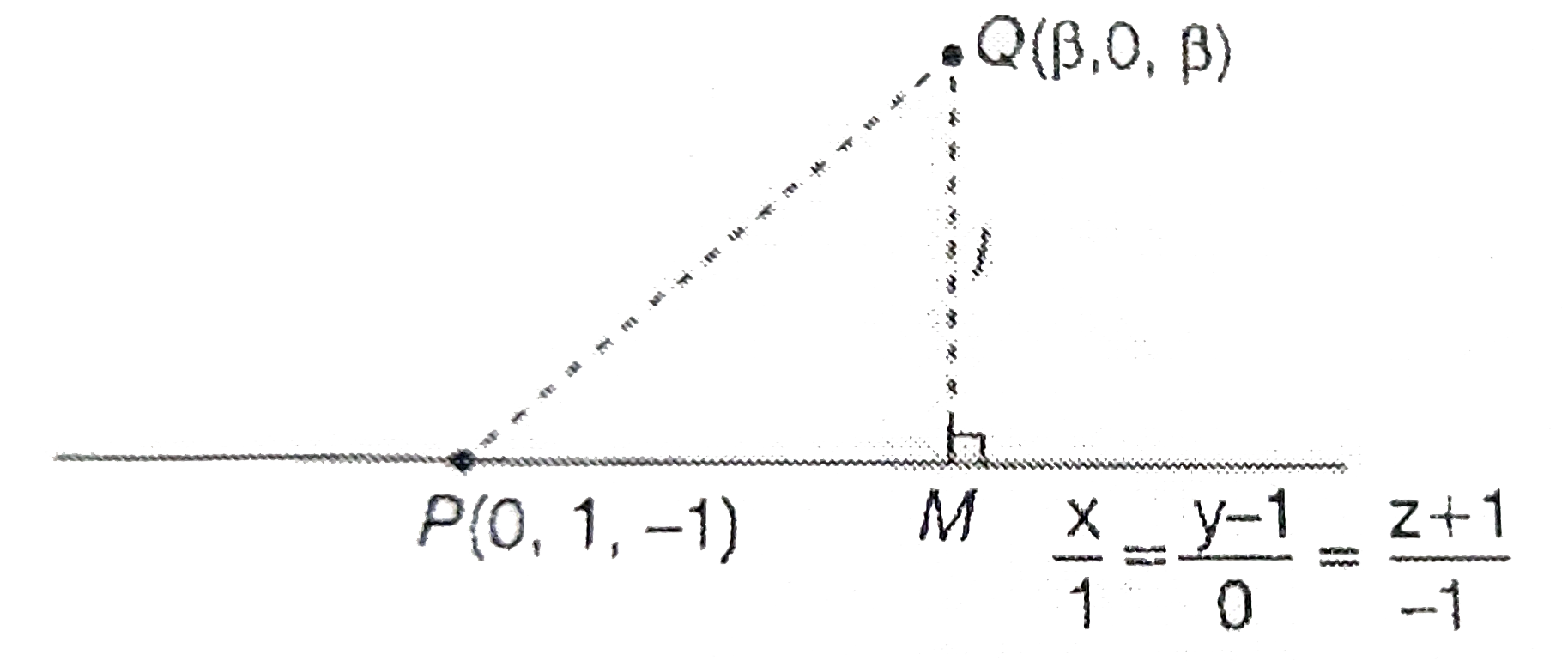
- if the length of the perpendicular from the point (beta,0,beta ...
Text Solution
|
- if alpha=(-1+sqrt(-3))/(2),beta=(-1-sqrt(-3))/(2) then prove that (alp...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha and beta are the roots of the equation x^(2)-2x-1=0. Find the...
Text Solution
|
- From point P(beta,0,beta), where (betane0) A perpendicular is drawn on...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha and beta be the roots of the equation x^(2)+x+1=0. Then for...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha and beta be the roots of the equation x^(2) + x + 1 = 0. ...
Text Solution
|
- if the length of the perpendicular from the point (beta,0,beta ...
Text Solution
|
- सिद्ध कीजिए की |{:(,1,x+alpha,y+z-alpha),(,1,y+beta,z+x-beta),(,1,z+y,...
Text Solution
|
- यदि alpha = ( - 1 + sqrt ( - 3 ) ) / ( 2 ) , beta = ( - 1- sq...
Text Solution
|