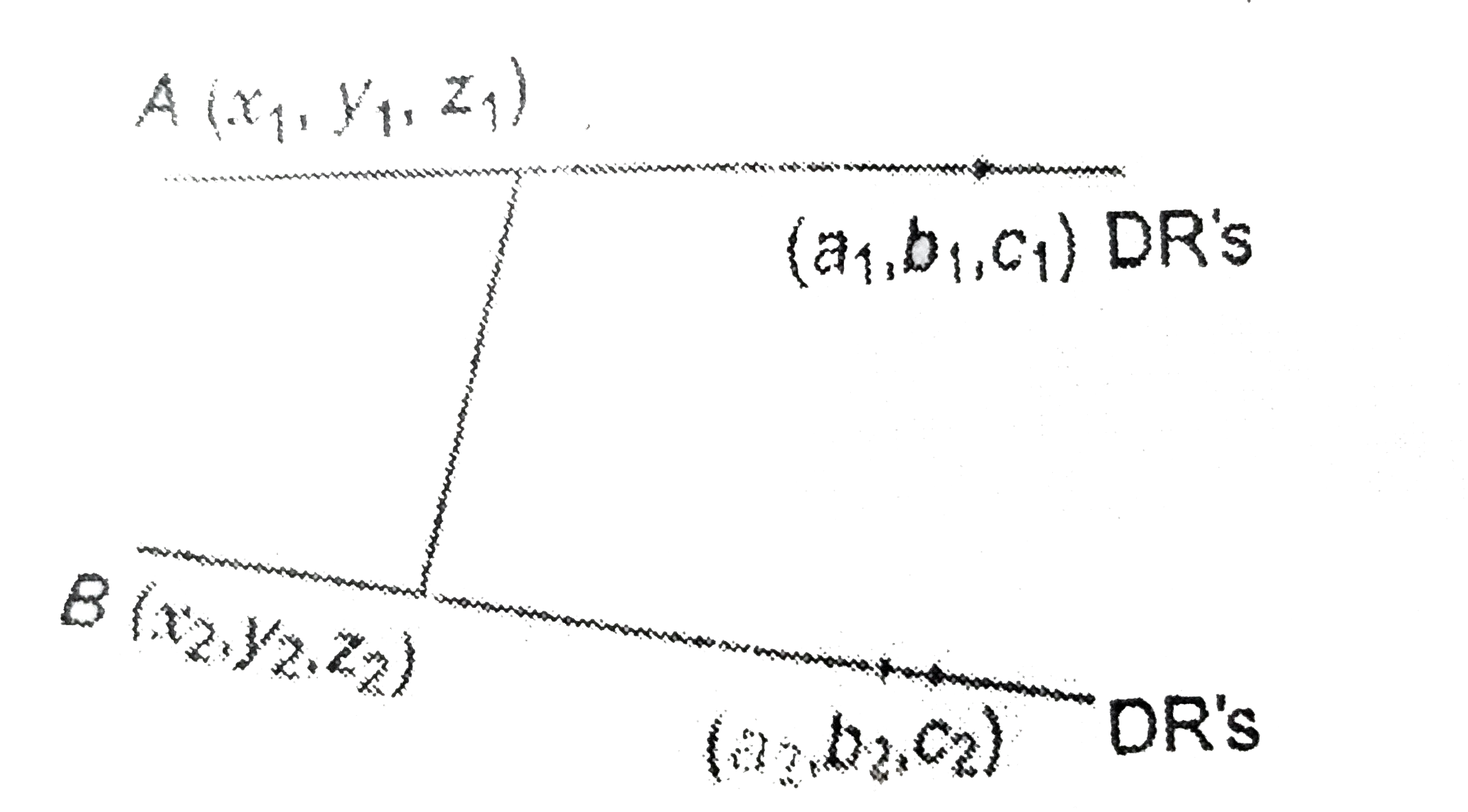
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two lines L1x=5, y/(3-alpha)=z/(-2)a n dL2: x=alphay/(-1)=z/(2-alpha) ...
Text Solution
|
- Two lines L(1):x=5,(y)/(3-alpha)=(z)/(-2) and L(2):x=alpha,(y)/(-1)=(z...
Text Solution
|
- Two lines L(1) : x=5, (y)/(3-alpha)=(z)/(-2) and L(2) : x=alpha, (y)/(...
Text Solution
|
- Two lines L(1): x = 5, (y)/(3-alpha) = (z)/(-2) and L(2) : x = alpha, ...
Text Solution
|
- The complete set of values of alpha for which the lines (x-1)/(2)=(y-2...
Text Solution
|
- दो रेखाएँ L(1):x=5, (y)/(3-alpha)=(z)/(-2) तथा L(2):x=alpha, (y)/(-1)...
Text Solution
|
- দুটি সরলরেখা L1 : x = 5, y/(3-alpha)=z/-2 এবং L2: x = alpha,y/-1=z/(2-...
Text Solution
|
- Two lines L1: x=5, y/(3-alpha)=z/(-2) and L2: x=alpha, y/(-1)=z/(2-alp...
Text Solution
|
- Two lines L1: x=5, y/(3-alpha)=z/(-2) and L2: x=alpha, y/(-1)=z/(2-alp...
Text Solution
|