PLAN It is based on two concepts one is intersection of straight line and plane and other is the foot of perpendicular from a point to the straight line.
Description of Situation
(i) If the staight line
`(x-x_(1))/(a)=(y-y_(1))/(b)=(z-z_(1))/(c)=lambda`
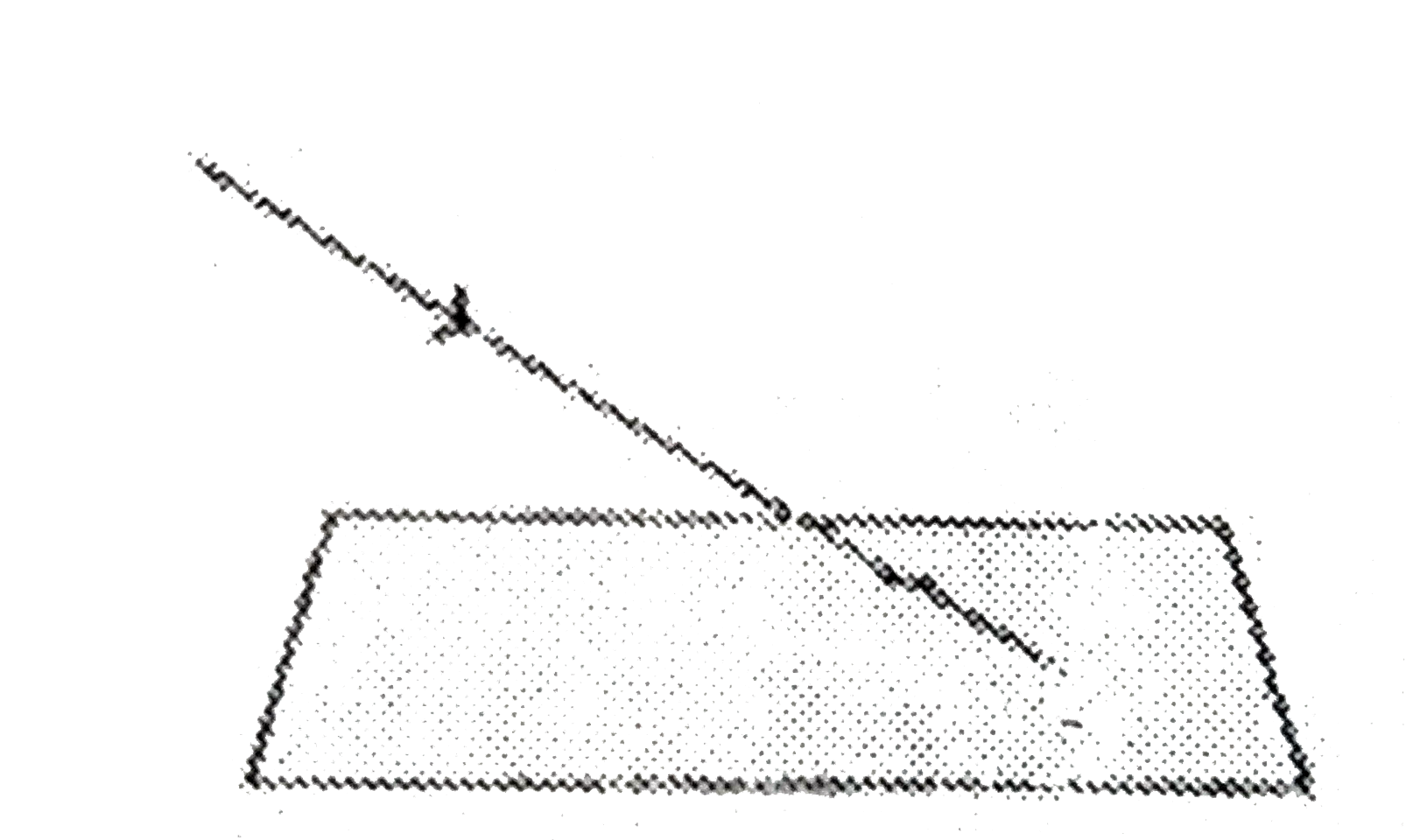
intersects the plane `Ax+By+Cz+d=0.`
Then, `(alambda+x_(1),blambda+y_(1),clambda+z_(1))` would satisfy
`Ax+By+Cz+d=0`
(ii) If A is the foot of perpendicular from P to `l`.
Then, (DR's of PA) is perpendicualr to DR's of `l`.
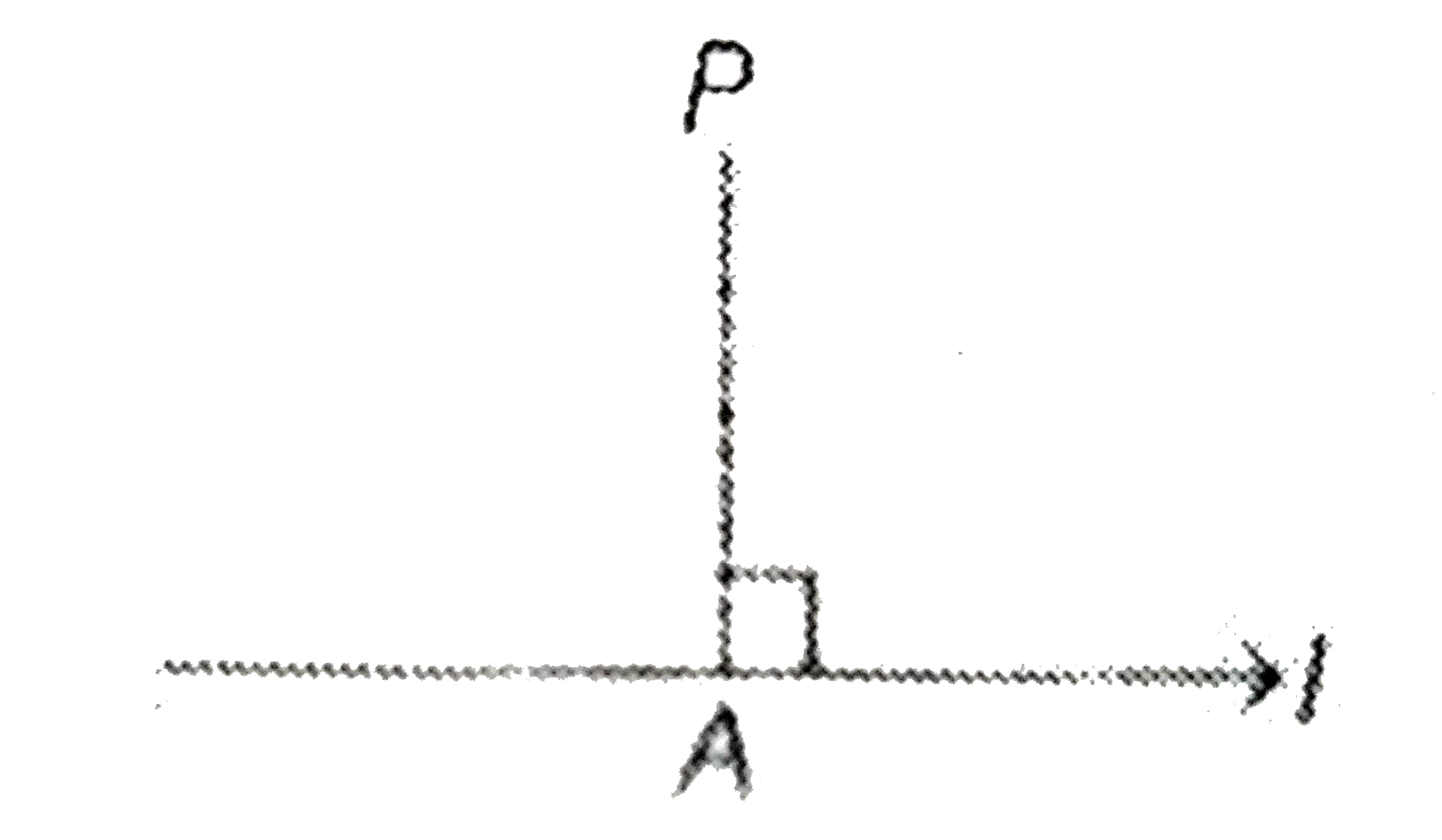
`implies" "bar(PA).bar(l)=0`
Equation of straight line QR, is
`(x+2)/(1-2)=(y-3)/(-1-3)=(z-5)/(-1)`
`implies" "(x-2)/(-1)=(y-3)/(-4)=(z-5)/(-1)`
`implies" "(x-2)/(1)=(y-3)/(4)=(z-5)/(1)=lambda...(i)`
`:.P(lambda+2,4lambda+3,lambda+5)" must lie on "5x-4y-z=1`
`implies" "5(lambda+2)-4(4lambda+3)-(lambda+5)=1`
`implies" "5lambda+10-16lambda-12-lambda-5=1`
`implies" "-7-12lambda=1`
`:." "lambda=(-2)/(3)`
or `" "P((4)/(3),(1)/(3), (13)/(3))`
Again, we can assume S from Eq. (i),
as `S(mu+2,4mu+3,mu+5)`
`:.DR's" of "TSltmu+2-2,4mu+3-1,mu+5-4gt`
`=ltmu,4mu+2,mu+1gt`
and DR's of `QR=lt1,4,1gt`
Since, perpendicualr
`:." "1(mu)+4(4mu+2)+1(mu+1)=0`
`implies" "mu=-(1)/(2)" and "S((3)/(2),1,(9)/(2))`
`:."Length of "PS=sqrt(((3)/(2)-(4)/(3))^(2)+(1-(1)/(3))^(2)+((9)/(2)-(13)/(3))^(2))=(1)/(sqrt(2))`

