A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
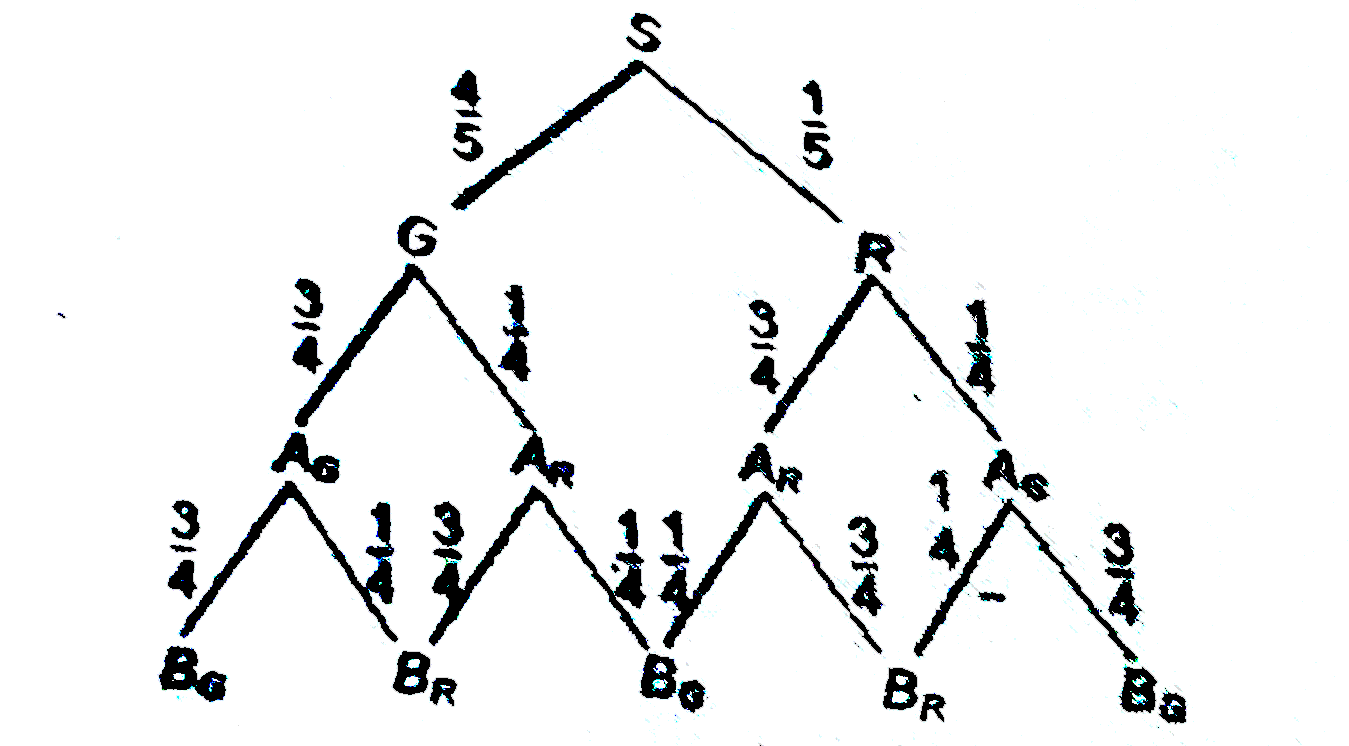
- A signal which can be green or red with probability 4/5 and 1/5 respec...
Text Solution
|
- A signal which can be green or red with probability 4/5 and 1/5 respec...
Text Solution
|
- Name the device fitted in the satellite which receives signals from Ea...
Text Solution
|
- A single which can can be green or red with probability 4/5 and 1/5 re...
Text Solution
|
- Due to economic reasons , only the upper sideband of an AM wave is tra...
Text Solution
|
- एक सिग्नल जिसके हरा अथवा लाल होने की प्रायिकताये क्रमशः (4)/(5) तथा (1...
Text Solution
|
- एक सिग्नल, जिसके हरा अथवा लाल होने की प्रायिकताएं क्रमशः 4/5 तथा 1/5 ह...
Text Solution
|
- A signal which can be green or red with probability 4/5 and 1/5 respec...
Text Solution
|
- A signal which can be green or red with probability 4/5 and 1/5 respec...
Text Solution
|