A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
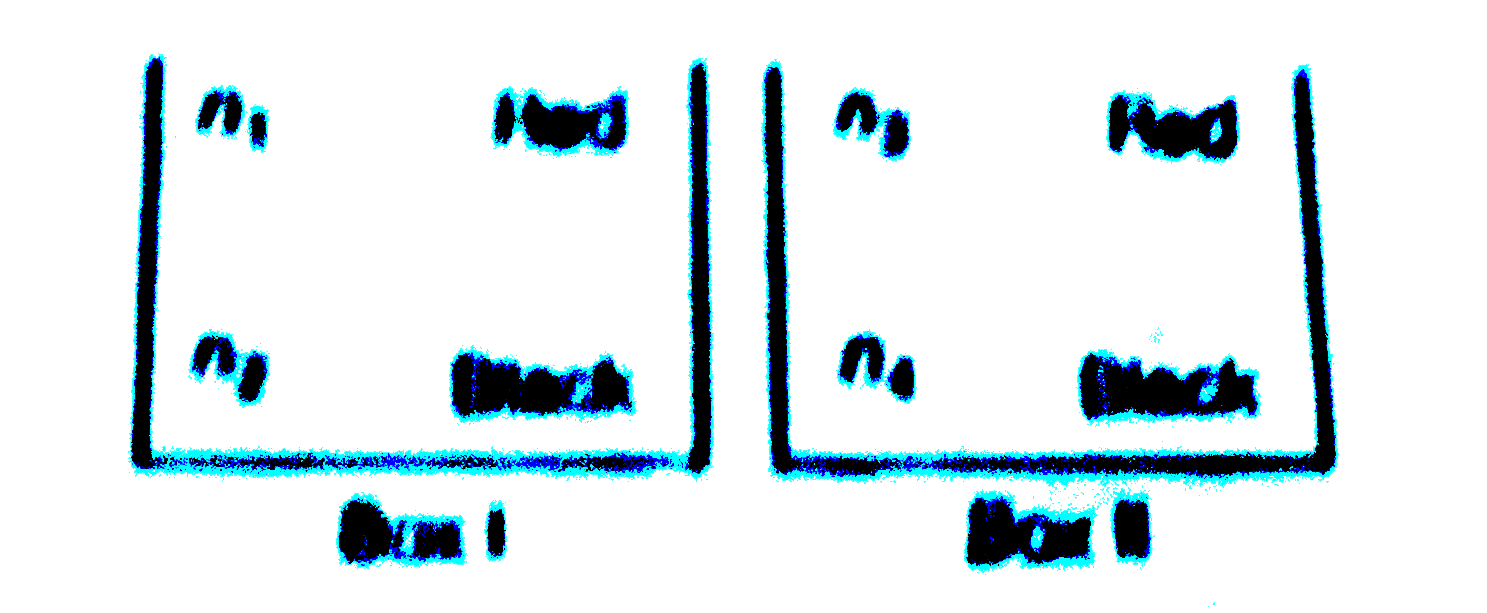
- Let n(1)and n(2) be the number of red and black balls, respectively, i...
Text Solution
|
- Let n1, and n2, be the number of red and black balls, respectively, i...
Text Solution
|
- Let n1, and n2, be the number of red and black balls, respectively, in...
Text Solution
|
- Let n(1)and n(2) be the number of red and black balls, respectively, i...
Text Solution
|
- Let n(1) "and" n(2) be the number of red and black balls, respectively...
Text Solution
|
- Let n(1) "and" n(2) be the number of red and black balls, respectively...
Text Solution
|
- माना कि बॉक्स I में n(1) लाल गेंद और n(2) काली गेंद है। माना कि बॉक्...
Text Solution
|
- माना कि बॉक्स I में n(1) लाल गेंद और n(2) काली गेंद है। माना कि बॉक्...
Text Solution
|
- Let n(1)and n(2) be the number of red and black balls, respectively, i...
Text Solution
|