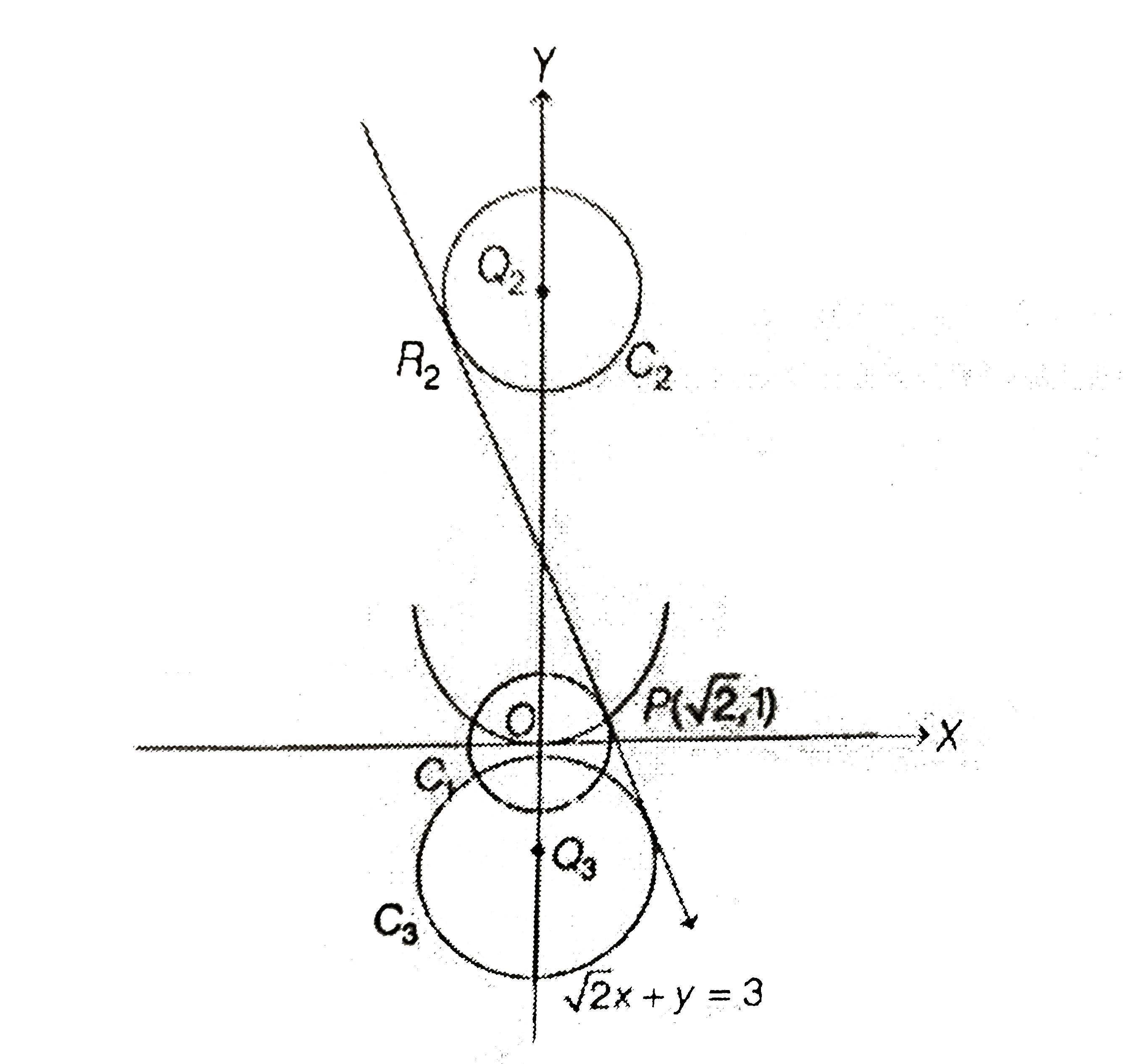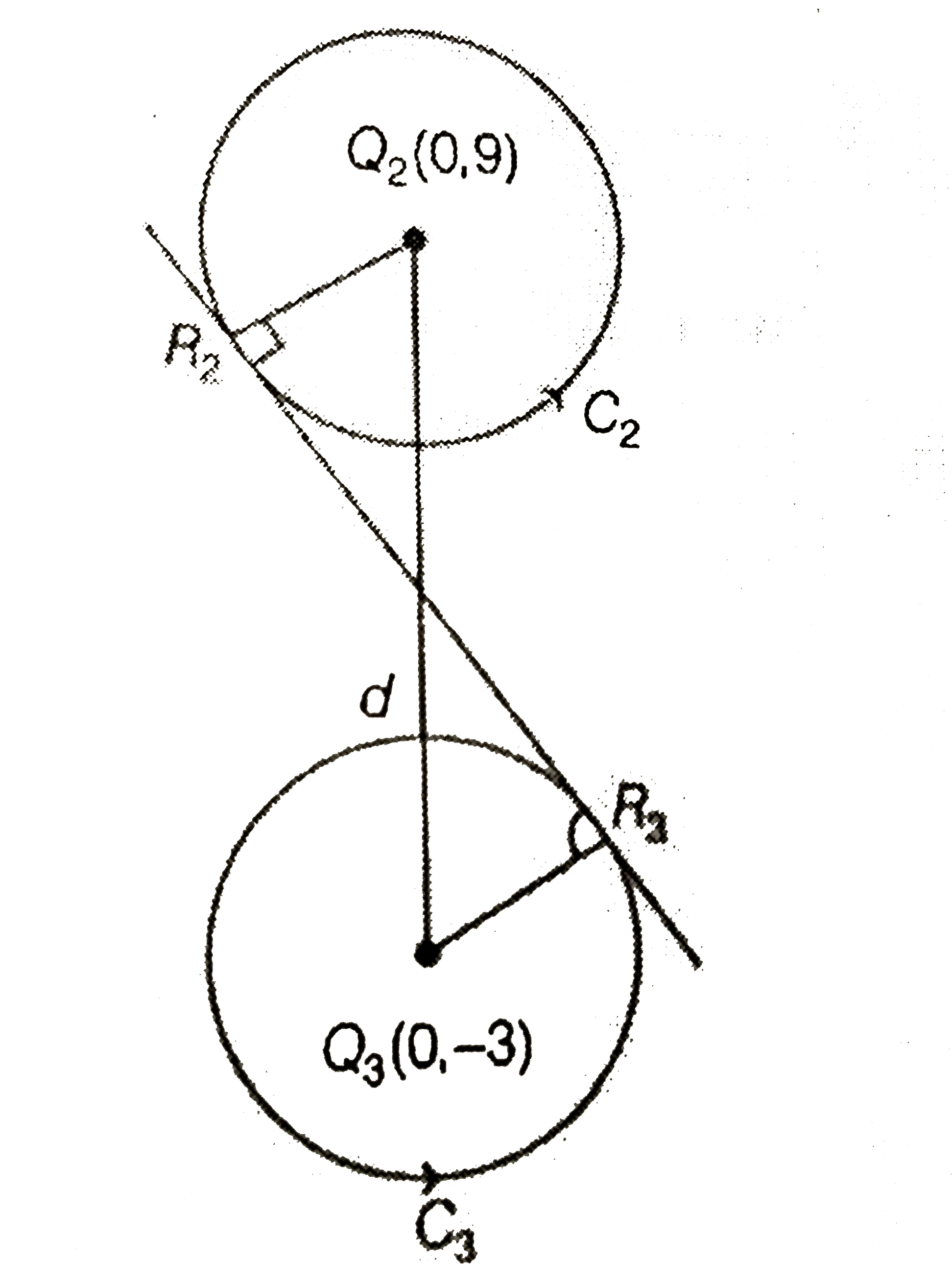A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The circle C(1):x^(2)+y^(2)=3, with centre at O, intersects the parabo...
Text Solution
|
- Three circles with centres C(1),C(2) and C(3) and radii r(1),r(2) and ...
Text Solution
|
- C1 is a circle of radius 1 touching the x- and the y-axis. C2 is anoth...
Text Solution
|
- In, the charges on C(1),C(2) , and C(3) , are Q(1), Q(2) , and Q(3) , ...
Text Solution
|
- Three circles C(1),C(2),C(3) with radii r(1),r(2),r(3)(r(1)ltr(2)ltr(3...
Text Solution
|
- Let C(1), C(2) be two circles touching each other externally at the p...
Text Solution
|
- The circle C(1):x^(2)+y^(2)=3, with centre at O, intersects the parabo...
Text Solution
|
- Consider circles C(1): x^(2) +y^(2) +2x - 2y +p = 0 C(2): x^(2) +y...
Text Solution
|
- The circle C(1) : x^(2)+y^(2)=3, with cenre at O, intersects the parab...
Text Solution
|