Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance. sqrt(3+...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance sqrt(3)+...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance.sqrt(3)+...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance sqrt3 + ...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 units are (sqrt3+1) units ...
Text Solution
|
- एक वृत्त जिसकी त्रिज्या 2 है , की दो समांतर जीवाओं के बीच की दूरी s...
Text Solution
|
- एक वृत्त जिसकी त्रिज्या 2 है, की दो समान्तर जीवाओं के बीच की दूरी sqrt...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance. sqrt(3+...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance sqrt3 + ...
Text Solution
|
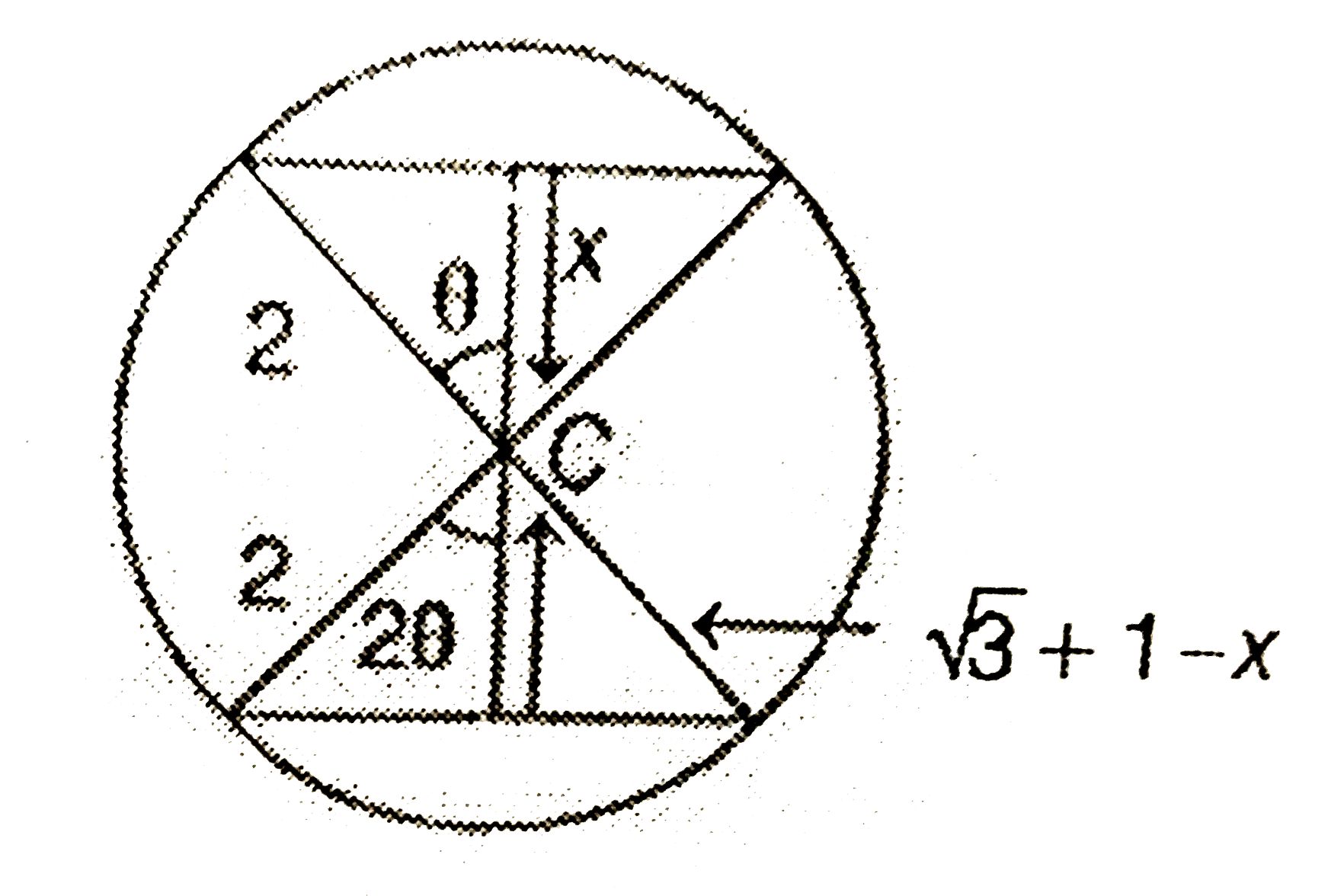 1
1